| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The significant recovery of solutes from the PCT lumen to the interstitial space creates an osmotic gradient that promotes water recovery. As noted before, water moves through channels created by the aquaporin proteins. These proteins are found in all cells in varying amounts and help regulate water movement across membranes and through cells by creating a passageway across the hydrophobic lipid bilayer membrane. Changing the number of aquaporin proteins in membranes of the collecting ducts also helps to regulate the osmolarity of the blood. The movement of many positively charged ions also creates an electrochemical gradient. This charge promotes the movement of negative ions toward the interstitial spaces and the movement of positive ions toward the lumen.
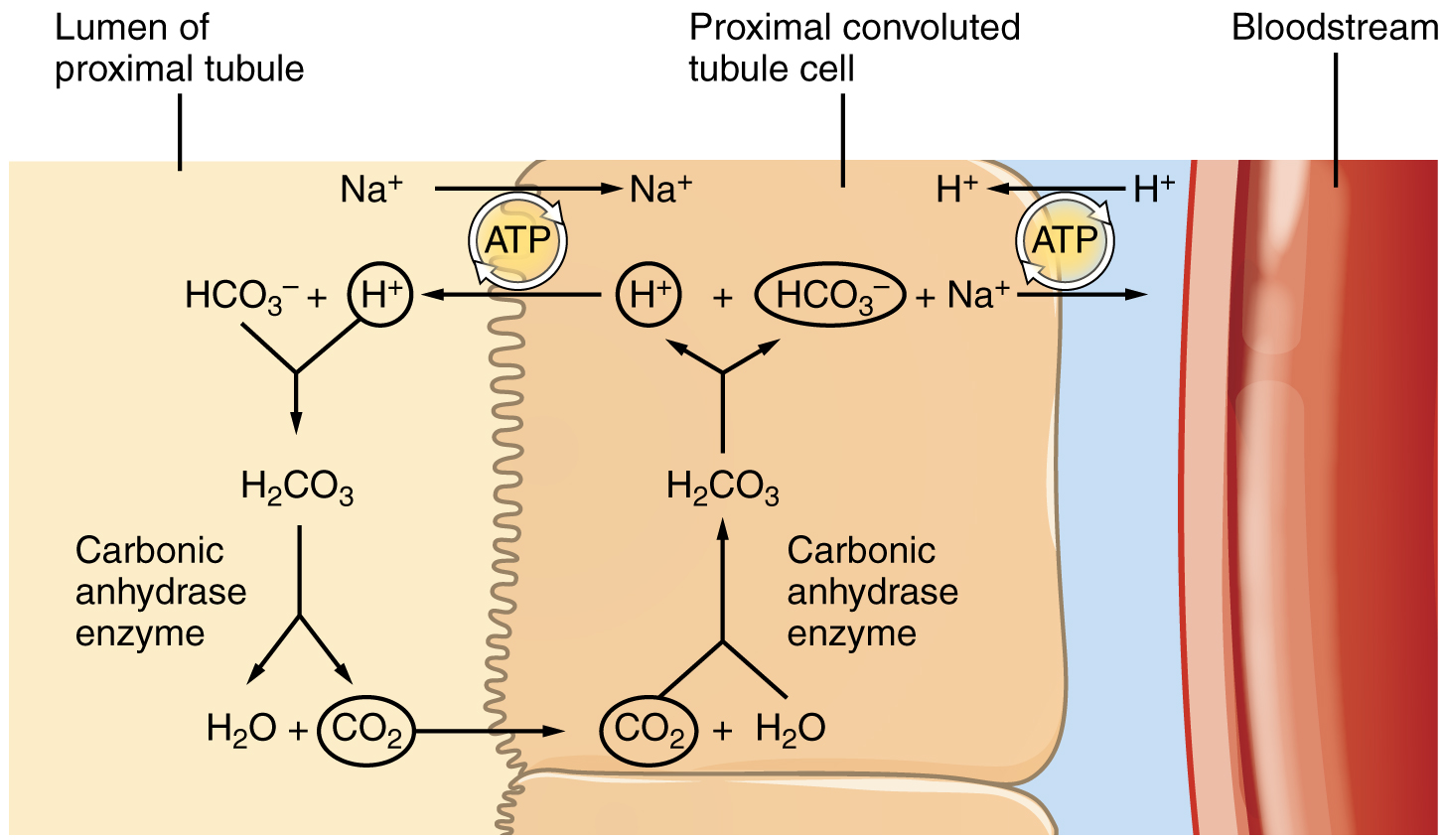
The loop of Henle consists of two sections: thick and thin descending and thin and thick ascending sections. The loops of cortical nephrons do not extend into the renal medulla very far, if at all. Juxtamedullary nephrons have loops that extend variable distances, some very deep into the medulla. The descending and ascending portions of the loop are highly specialized to enable recovery of much of the Na + and water that were filtered by the glomerulus. As the forming urine moves through the loop, the osmolarity will change from isosmotic with blood (about 278–300 mOsmol/kg) to both a very hypertonic solution of about 1200 mOsmol/kg and a very hypotonic solution of about 100 mOsmol/kg. These changes are accomplished by osmosis in the descending limb and active transport in the ascending limb. Solutes and water recovered from these loops are returned to the circulation by way of the vasa recta.
The majority of the descending loop is comprised of simple squamous epithelial cells; to simplify the function of the loop, this discussion focuses on these cells. These membranes have permanent aquaporin channel proteins that allow unrestricted movement of water from the descending loop into the surrounding interstitium as osmolarity increases from about 300 mOsmol/kg to about 1200 mOsmol/kg. This increase results in reabsorption of up to 15 percent of the water entering the nephron. Modest amounts of urea, Na + , and other ions are also recovered here.
Most of the solutes that were filtered in the glomerulus have now been recovered along with a majority of water, about 82 percent. As the forming urine enters the ascending loop, major adjustments will be made to the concentration of solutes to create what you perceive as urine.
The ascending loop is made of very short thin and longer thick portions. Once again, to simplify the function, this section only considers the thick portion. The thick portion is lined with simple cuboidal epithelium without a brush border. It is completely impermeable to water due to the absence of aquaporin proteins, but ions, mainly Na + , are actively pumped out of the loop by large quantities of the Na +/ K + ATPase pump. This has two significant effects: Removal of Na + while retaining water leads to a hypotonic filtrate by the time it reaches the DCT; pumping Na + into the interstitial space contributes to the hyperosmotic environment in the kidney medulla.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?