| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The posterior muscles of the neck are primarily concerned with head movements, like extension. The back muscles stabilize and move the vertebral column, and are grouped according to the lengths and direction of the fascicles.
The splenius muscles originate at the midline and run laterally and superiorly to their insertions. From the sides and the back of the neck, the splenius capitis inserts onto the head region, and the splenius cervicis extends onto the cervical region. These muscles can extend the head, laterally flex it, and rotate it ( [link] ).
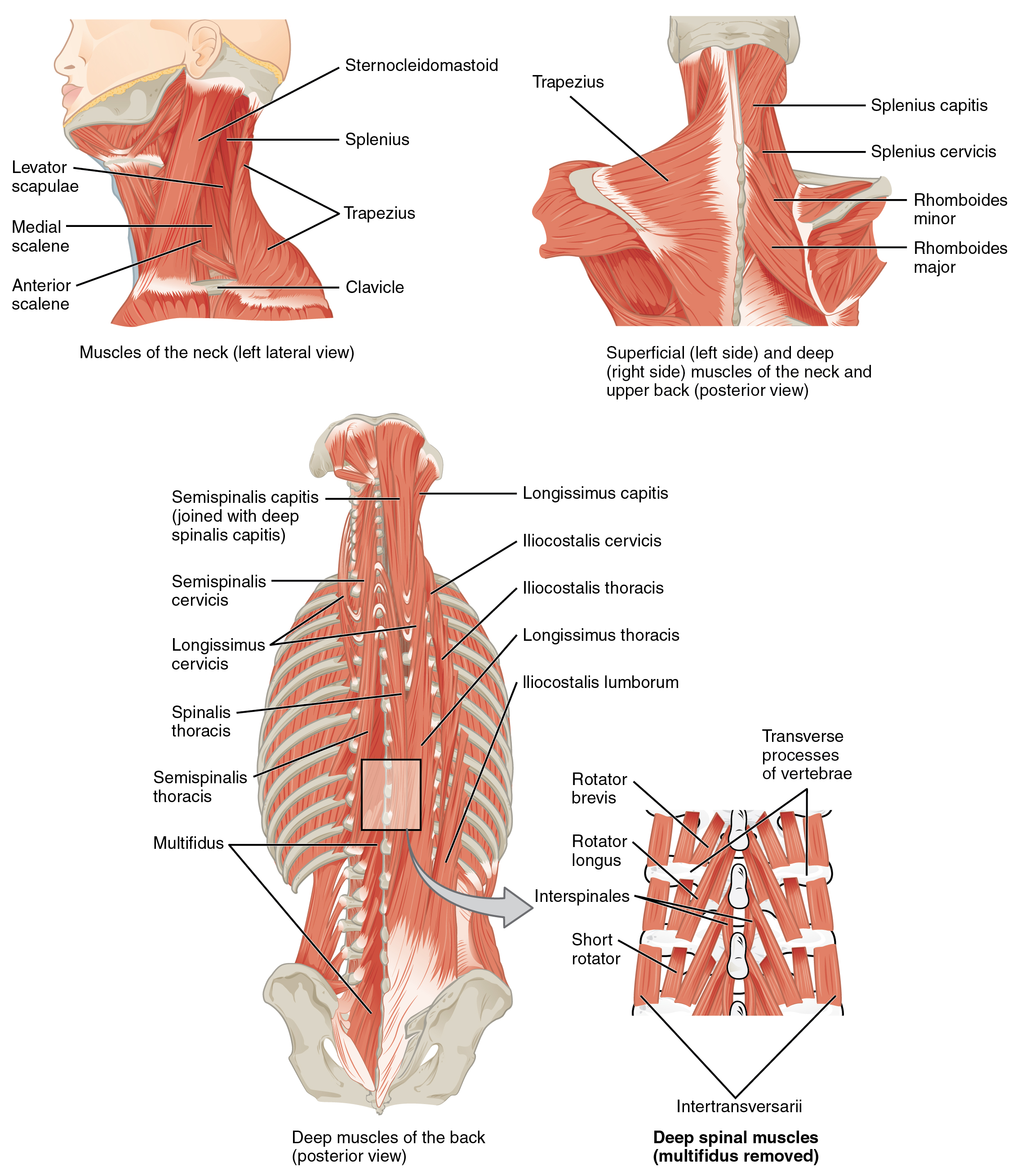
The erector spinae group forms the majority of the muscle mass of the back and it is the primary extensor of the vertebral column. It controls flexion, lateral flexion, and rotation of the vertebral column, and maintains the lumbar curve. The erector spinae comprises the iliocostalis (laterally placed) group, the longissimus (intermediately placed) group, and the spinalis (medially placed) group.
The iliocostalis group includes the iliocostalis cervicis , associated with the cervical region; the iliocostalis thoracis , associated with the thoracic region; and the iliocostalis lumborum , associated with the lumbar region. The three muscles of the longissimus group are the longissimus capitis , associated with the head region; the longissimus cervicis , associated with the cervical region; and the longissimus thoracis , associated with the thoracic region. The third group, the spinalis group , comprises the spinalis capitis (head region), the spinalis cervicis (cervical region), and the spinalis thoracis (thoracic region).
The transversospinales muscles run from the transverse processes to the spinous processes of the vertebrae. Similar to the erector spinae muscles, the semispinalis muscles in this group are named for the areas of the body with which they are associated. The semispinalis muscles include the semispinalis capitis , the semispinalis cervicis , and the semispinalis thoracis . The multifidus muscle of the lumbar region helps extend and laterally flex the vertebral column.
Important in the stabilization of the vertebral column is the segmental muscle group , which includes the interspinales and intertransversarii muscles. These muscles bring together the spinous and transverse processes of each consecutive vertebra. Finally, the scalene muscles work together to flex, laterally flex, and rotate the head. They also contribute to deep inhalation. The scalene muscles include the anterior scalene muscle (anterior to the middle scalene), the middle scalene muscle (the longest, intermediate between the anterior and posterior scalenes), and the posterior scalene muscle (the smallest, posterior to the middle scalene).
Muscles are either axial muscles or appendicular. The axial muscles are grouped based on location, function, or both. Some axial muscles cross over to the appendicular skeleton. The muscles of the head and neck are all axial. The muscles in the face create facial expression by inserting into the skin rather than onto bone. Muscles that move the eyeballs are extrinsic, meaning they originate outside of the eye and insert onto it. Tongue muscles are both extrinsic and intrinsic. The genioglossus depresses the tongue and moves it anteriorly; the styloglossus lifts the tongue and retracts it; the palatoglossus elevates the back of the tongue; and the hyoglossus depresses and flattens it. The muscles of the anterior neck facilitate swallowing and speech, stabilize the hyoid bone and position the larynx. The muscles of the neck stabilize and move the head. The sternocleidomastoid divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles.
The muscles of the back and neck that move the vertebral column are complex, overlapping, and can be divided into five groups. The splenius group includes the splenius capitis and the splenius cervicis. The erector spinae has three subgroups. The iliocostalis group includes the iliocostalis cervicis, the iliocostalis thoracis, and the iliocostalis lumborum. The longissimus group includes the longissimus capitis, the longissimus cervicis, and the longissimus thoracis. The spinalis group includes the spinalis capitis, the spinalis cervicis, and the spinalis thoracis. The transversospinales include the semispinalis capitis, semispinalis cervicis, semispinalis thoracis, multifidus, and rotatores. The segmental muscles include the interspinales and intertransversarii. Finally, the scalenes include the anterior scalene, middle scalene, and posterior scalene.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?