| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
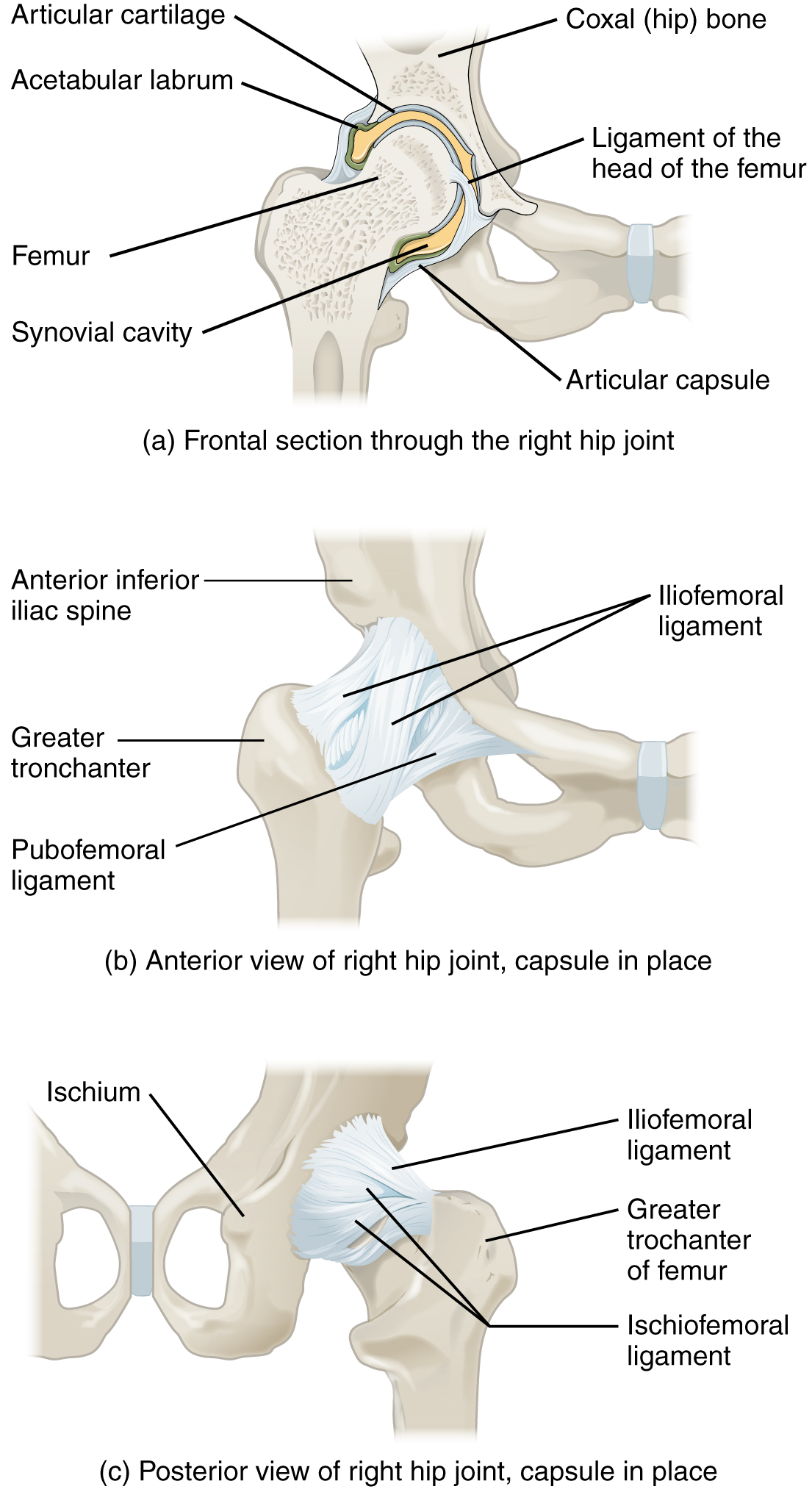
Watch this video for a tutorial on the anatomy of the hip joint. What is a possible consequence following a fracture of the femoral neck within the capsule of the hip joint?
Watch this video to learn more about the anatomy of the hip joint, including bones, joints, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels. Where is the articular cartilage thickest within the hip joint?
The knee joint is the largest joint of the body ( [link] ). It actually consists of three articulations. The femoropatellar joint is found between the patella and the distal femur. The medial tibiofemoral joint and lateral tibiofemoral joint are located between the medial and lateral condyles of the femur and the medial and lateral condyles of the tibia. All of these articulations are enclosed within a single articular capsule. The knee functions as a hinge joint, allowing flexion and extension of the leg. This action is generated by both rolling and gliding motions of the femur on the tibia. In addition, some rotation of the leg is available when the knee is flexed, but not when extended. The knee is well constructed for weight bearing in its extended position, but is vulnerable to injuries associated with hyperextension, twisting, or blows to the medial or lateral side of the joint, particularly while weight bearing.
At the femoropatellar joint, the patella slides vertically within a groove on the distal femur. The patella is a sesamoid bone incorporated into the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle, the large muscle of the anterior thigh. The patella serves to protect the quadriceps tendon from friction against the distal femur. Continuing from the patella to the anterior tibia just below the knee is the patellar ligament . Acting via the patella and patellar ligament, the quadriceps femoris is a powerful muscle that acts to extend the leg at the knee. It also serves as a “dynamic ligament” to provide very important support and stabilization for the knee joint.
The medial and lateral tibiofemoral joints are the articulations between the rounded condyles of the femur and the relatively flat condyles of the tibia. During flexion and extension motions, the condyles of the femur both roll and glide over the surfaces of the tibia. The rolling action produces flexion or extension, while the gliding action serves to maintain the femoral condyles centered over the tibial condyles, thus ensuring maximal bony, weight-bearing support for the femur in all knee positions. As the knee comes into full extension, the femur undergoes a slight medial rotation in relation to tibia. The rotation results because the lateral condyle of the femur is slightly smaller than the medial condyle. Thus, the lateral condyle finishes its rolling motion first, followed by the medial condyle. The resulting small medial rotation of the femur serves to “lock” the knee into its fully extended and most stable position. Flexion of the knee is initiated by a slight lateral rotation of the femur on the tibia, which “unlocks” the knee. This lateral rotation motion is produced by the popliteus muscle of the posterior leg.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?