| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The upper limb is divided into three regions. These consist of the arm , located between the shoulder and elbow joints; the forearm , which is between the elbow and wrist joints; and the hand , which is located distal to the wrist. There are 30 bones in each upper limb (see [link] ). The humerus is the single bone of the upper arm, and the ulna (medially) and the radius (laterally) are the paired bones of the forearm. The base of the hand contains eight bones, each called a carpal bone , and the palm of the hand is formed by five bones, each called a metacarpal bone . The fingers and thumb contain a total of 14 bones, each of which is a phalanx bone of the hand .
The humerus is the single bone of the upper arm region ( [link] ). At its proximal end is the head of the humerus . This is the large, round, smooth region that faces medially. The head articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula to form the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint. The margin of the smooth area of the head is the anatomical neck of the humerus. Located on the lateral side of the proximal humerus is an expanded bony area called the greater tubercle . The smaller lesser tubercle of the humerus is found on the anterior aspect of the humerus. Both the greater and lesser tubercles serve as attachment sites for muscles that act across the shoulder joint. Passing between the greater and lesser tubercles is the narrow intertubercular groove (sulcus) , which is also known as the bicipital groove because it provides passage for a tendon of the biceps brachii muscle. The surgical neck is located at the base of the expanded, proximal end of the humerus, where it joins the narrow shaft of the humerus . The surgical neck is a common site of arm fractures. The deltoid tuberosity is a roughened, V-shaped region located on the lateral side in the middle of the humerus shaft. As its name indicates, it is the site of attachment for the deltoid muscle.
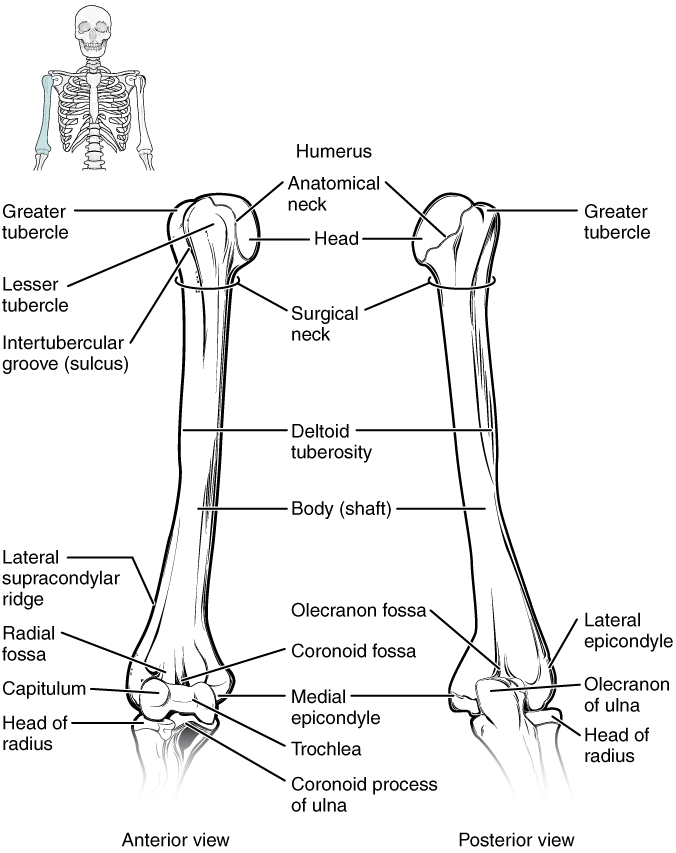
Distally, the humerus becomes flattened. The prominent bony projection on the medial side is the medial epicondyle of the humerus . The much smaller lateral epicondyle of the humerus is found on the lateral side of the distal humerus. The roughened ridge of bone above the lateral epicondyle is the lateral supracondylar ridge . All of these areas are attachment points for muscles that act on the forearm, wrist, and hand. The powerful grasping muscles of the anterior forearm arise from the medial epicondyle, which is thus larger and more robust than the lateral epicondyle that gives rise to the weaker posterior forearm muscles.
The distal end of the humerus has two articulation areas, which join the ulna and radius bones of the forearm to form the elbow joint . The more medial of these areas is the trochlea , a spindle- or pulley-shaped region (trochlea = “pulley”), which articulates with the ulna bone. Immediately lateral to the trochlea is the capitulum (“small head”), a knob-like structure located on the anterior surface of the distal humerus. The capitulum articulates with the radius bone of the forearm. Just above these bony areas are two small depressions. These spaces accommodate the forearm bones when the elbow is fully bent (flexed). Superior to the trochlea is the coronoid fossa , which receives the coronoid process of the ulna, and above the capitulum is the radial fossa , which receives the head of the radius when the elbow is flexed. Similarly, the posterior humerus has the olecranon fossa , a larger depression that receives the olecranon process of the ulna when the forearm is fully extended.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?