| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A fracture is a broken bone. It will heal whether or not a physician resets it in its anatomical position. If the bone is not reset correctly, the healing process will keep the bone in its deformed position.
When a broken bone is manipulated and set into its natural position without surgery, the procedure is called a closed reduction . Open reduction requires surgery to expose the fracture and reset the bone. While some fractures can be minor, others are quite severe and result in grave complications. For example, a fractured diaphysis of the femur has the potential to release fat globules into the bloodstream. These can become lodged in the capillary beds of the lungs, leading to respiratory distress and if not treated quickly, death.
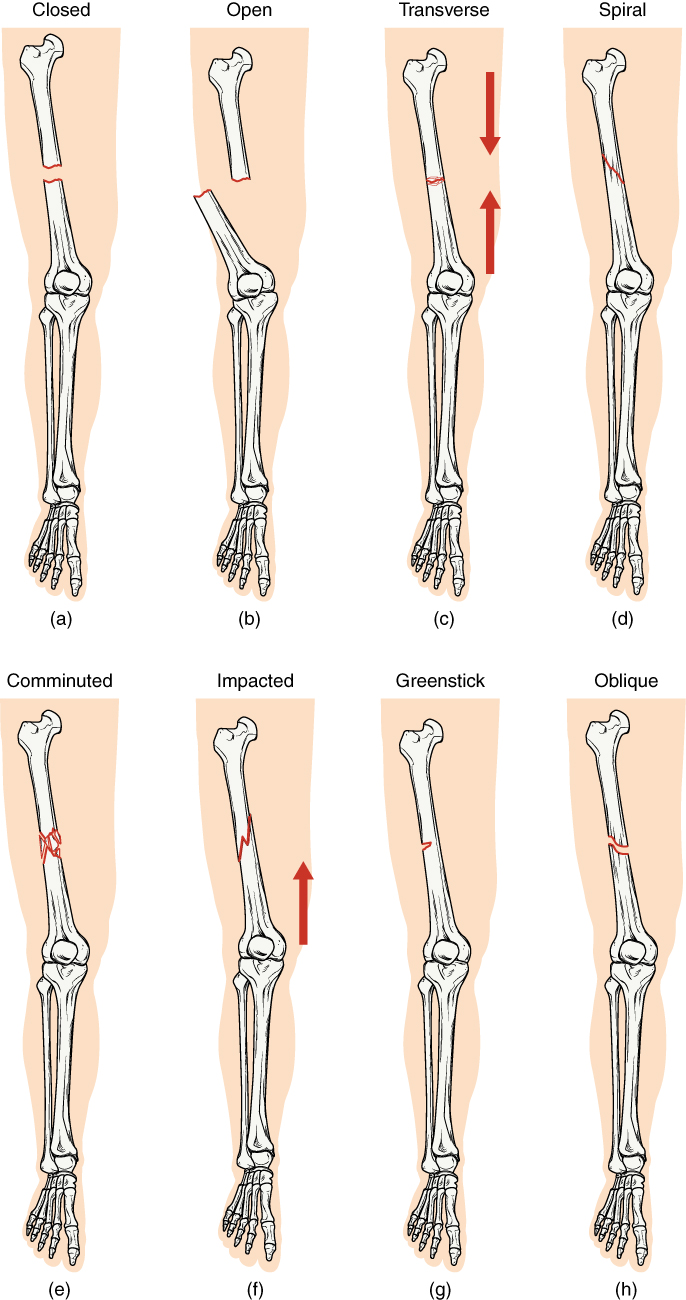
Fractures are classified by their complexity, location, and other features ( [link] ). [link] outlines common types of fractures. Some fractures may be described using more than one term because it may have the features of more than one type (e.g., an open transverse fracture).
| Types of Fractures | |
|---|---|
| Type of fracture | Description |
| Transverse | Occurs straight across the long axis of the bone |
| Oblique | Occurs at an angle that is not 90 degrees |
| Spiral | Bone segments are pulled apart as a result of a twisting motion |
| Comminuted | Several breaks result in many small pieces between two large segments |
| Impacted | One fragment is driven into the other, usually as a result of compression |
| Greenstick | A partial fracture in which only one side of the bone is broken |
| Open (or compound) | A fracture in which at least one end of the broken bone tears through the skin; carries a high risk of infection |
| Closed (or simple) | A fracture in which the skin remains intact |
When a bone breaks, blood flows from any vessel torn by the fracture. These vessels could be in the periosteum, osteons, and/or medullary cavity. The blood begins to clot, and about six to eight hours after the fracture, the clotting blood has formed a fracture hematoma ( [link] a ). The disruption of blood flow to the bone results in the death of bone cells around the fracture.
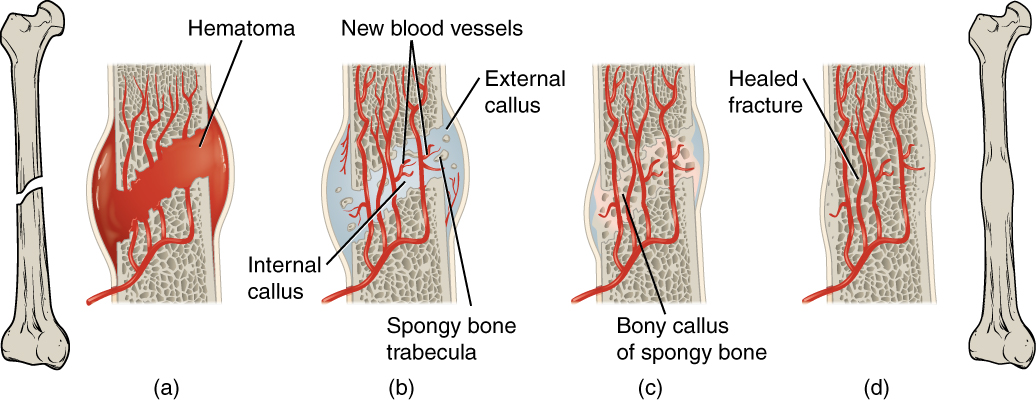
Within about 48 hours after the fracture, chondrocytes from the endosteum have created an internal callus (plural = calli) by secreting a fibrocartilaginous matrix between the two ends of the broken bone, while the periosteal chondrocytes and osteoblasts create an external callus of hyaline cartilage and bone, respectively, around the outside of the break ( [link] b ). This stabilizes the fracture.
Over the next several weeks, osteoclasts resorb the dead bone; osteogenic cells become active, divide, and differentiate into osteoblasts. The cartilage in the calli is replaced by trabecular bone via endochondral ossification ( [link] c ).
Eventually, the internal and external calli unite, compact bone replaces spongy bone at the outer margins of the fracture, and healing is complete. A slight swelling may remain on the outer surface of the bone, but quite often, that region undergoes remodeling ( [link] d ), and no external evidence of the fracture remains.
Visit this website to review different types of fractures and then take a short self-assessment quiz.
Fractured bones may be repaired by closed reduction or open reduction. Fractures are classified by their complexity, location, and other features. Common types of fractures are transverse, oblique, spiral, comminuted, impacted, greenstick, open (or compound), and closed (or simple). Healing of fractures begins with the formation of a hematoma, followed by internal and external calli. Osteoclasts resorb dead bone, while osteoblasts create new bone that replaces the cartilage in the calli. The calli eventually unite, remodeling occurs, and healing is complete.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?