| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although the small intestine is the workhorse of the system, where the majority of digestion occurs, and where most of the released nutrients are absorbed into the blood or lymph, each of the digestive system organs makes a vital contribution to this process ( [link] ).
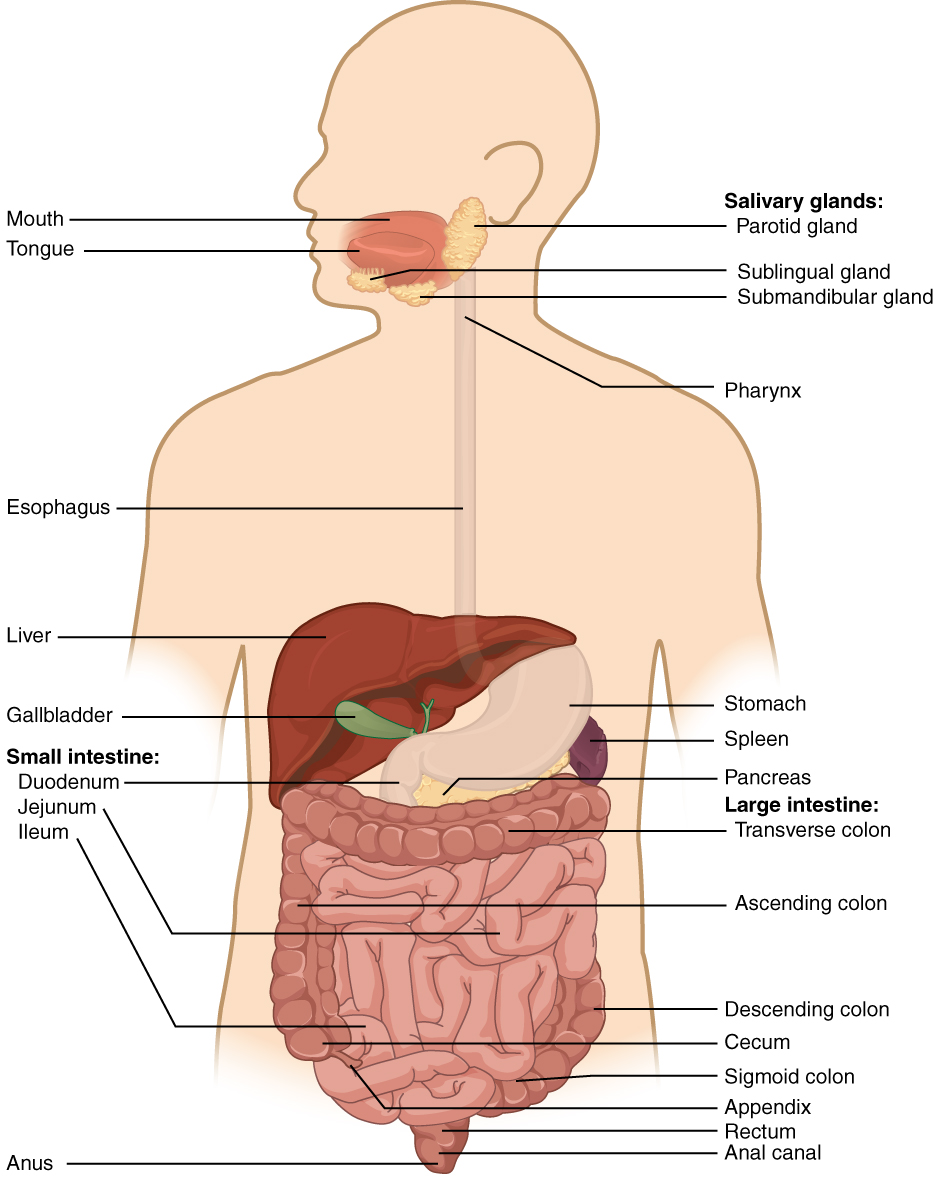
As is the case with all body systems, the digestive system does not work in isolation; it functions cooperatively with the other systems of the body. Consider for example, the interrelationship between the digestive and cardiovascular systems. Arteries supply the digestive organs with oxygen and processed nutrients, and veins drain the digestive tract. These intestinal veins, constituting the hepatic portal system, are unique; they do not return blood directly to the heart. Rather, this blood is diverted to the liver where its nutrients are off-loaded for processing before blood completes its circuit back to the heart. At the same time, the digestive system provides nutrients to the heart muscle and vascular tissue to support their functioning. The interrelationship of the digestive and endocrine systems is also critical. Hormones secreted by several endocrine glands, as well as endocrine cells of the pancreas, the stomach, and the small intestine, contribute to the control of digestion and nutrient metabolism. In turn, the digestive system provides the nutrients to fuel endocrine function. [link] gives a quick glimpse at how these other systems contribute to the functioning of the digestive system.
| Contribution of Other Body Systems to the Digestive System | |
|---|---|
| Body system | Benefits received by the digestive system |
| Cardiovascular | Blood supplies digestive organs with oxygen and processed nutrients |
| Endocrine | Endocrine hormones help regulate secretion in digestive glands and accessory organs |
| Integumentary | Skin helps protect digestive organs and synthesizes vitamin D for calcium absorption |
| Lymphatic | Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue and other lymphatic tissue defend against entry of pathogens; lacteals absorb lipids; and lymphatic vessels transport lipids to bloodstream |
| Muscular | Skeletal muscles support and protect abdominal organs |
| Nervous | Sensory and motor neurons help regulate secretions and muscle contractions in the digestive tract |
| Respiratory | Respiratory organs provide oxygen and remove carbon dioxide |
| Skeletal | Bones help protect and support digestive organs |
| Urinary | Kidneys convert vitamin D into its active form, allowing calcium absorption in the small intestine |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?