| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In a developing embryo,the heart has developed enough by day 21 post-fertilization to begin beating. Circulation patterns are clearly established by the fourth week of embryonic life. It is critical to the survival of the developing human that the circulatory system forms early to supply the growing tissue with nutrients and gases, and to remove waste products. Blood cells and vessel production in structures outside the embryo proper called the yolk sac, chorion, and connecting stalk begin about 15 to 16 days following fertilization. Development of these circulatory elements within the embryo itself begins approximately 2 days later. You will learn more about the formation and function of these early structures when you study the chapter on development. During those first few weeks, blood vessels begin to form from the embryonic mesoderm. The precursor cells are known as hemangioblasts . These in turn differentiate into angioblasts , which give rise to the blood vessels and pluripotent stem cells, which differentiate into the formed elements of blood. (Seek additional content for more detail on fetal development and circulation.) Together, these cells form masses known as blood islands scattered throughout the embryonic disc. Spaces appear on the blood islands that develop into vessel lumens. The endothelial lining of the vessels arise from the angioblasts within these islands. Surrounding mesenchymal cells give rise to the smooth muscle and connective tissue layers of the vessels. While the vessels are developing, the pluripotent stem cells begin to form the blood.
Vascular tubes also develop on the blood islands, and they eventually connect to one another as well as to the developing, tubular heart. Thus, the developmental pattern, rather than beginning from the formation of one central vessel and spreading outward, occurs in many regions simultaneously with vessels later joining together. This angiogenesis —the creation of new blood vessels from existing ones—continues as needed throughout life as we grow and develop.
Blood vessel development often follows the same pattern as nerve development and travels to the same target tissues and organs. This occurs because the many factors directing growth of nerves also stimulate blood vessels to follow a similar pattern. Whether a given vessel develops into an artery or a vein is dependent upon local concentrations of signaling proteins.
As the embryo grows within the mother’s uterus, its requirements for nutrients and gas exchange also grow. The placenta—a circulatory organ unique to pregnancy—develops jointly from the embryo and uterine wall structures to fill this need. Emerging from the placenta is the umbilical vein , which carries oxygen-rich blood from the mother to the fetal inferior vena cava via the ductus venosus to the heart that pumps it into fetal circulation. Two umbilical arteries carry oxygen-depleted fetal blood, including wastes and carbon dioxide, to the placenta. Remnants of the umbilical arteries remain in the adult. (Seek additional content for more information on the role of the placenta in fetal circulation.)
There are three major shunts—alternate paths for blood flow—found in the circulatory system of the fetus. Two of these shunts divert blood from the pulmonary to the systemic circuit, whereas the third connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava. The first two shunts are critical during fetal life, when the lungs are compressed, filled with amniotic fluid, and nonfunctional, and gas exchange is provided by the placenta. These shunts close shortly after birth, however, when the newborn begins to breathe. The third shunt persists a bit longer but becomes nonfunctional once the umbilical cord is severed. The three shunts are as follows ( [link] ):
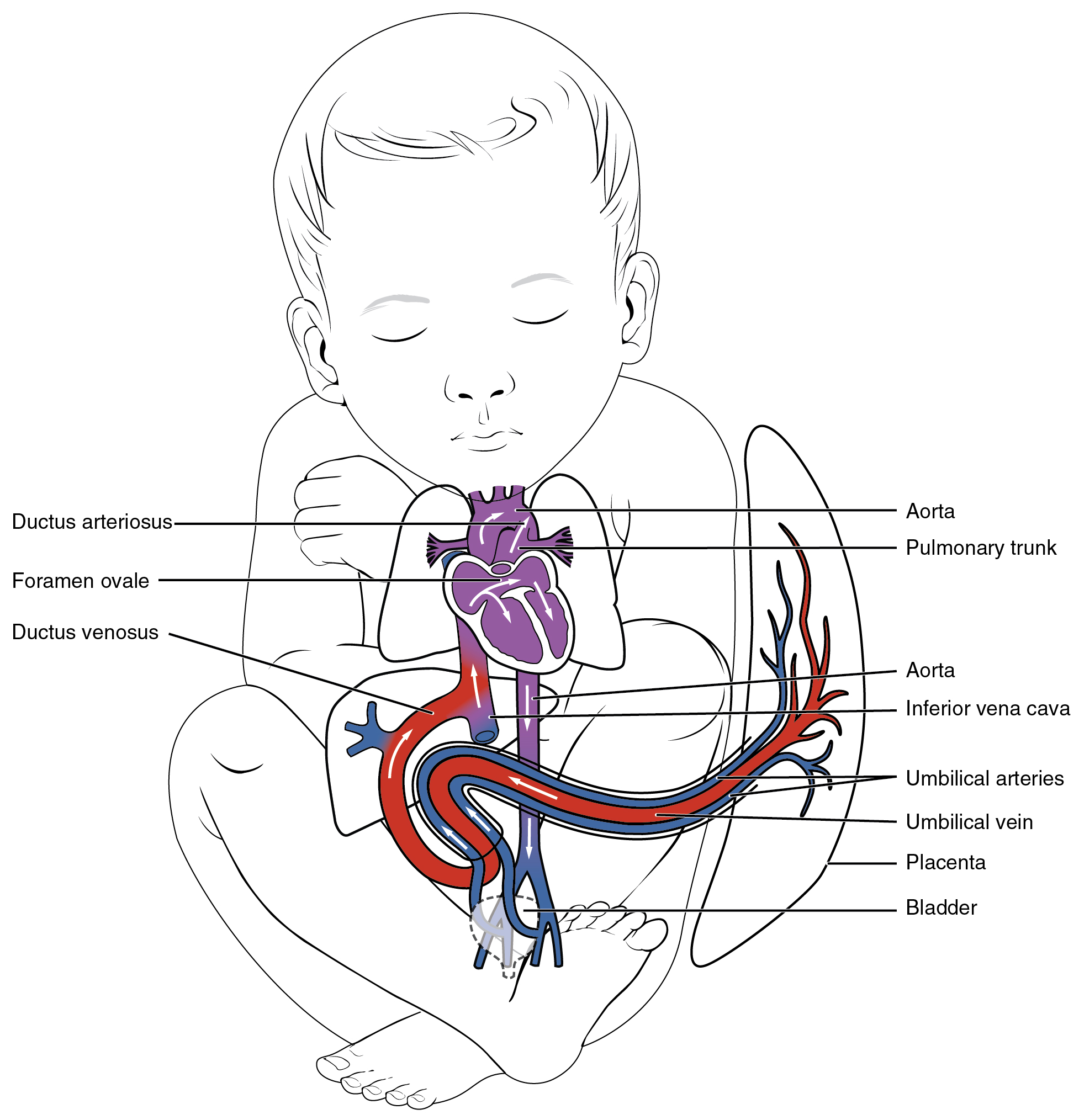
Blood vessels begin to form from the embryonic mesoderm. The precursor hemangioblasts differentiate into angioblasts, which give rise to the blood vessels and pluripotent stem cells that differentiate into the formed elements of the blood. Together, these cells form blood islands scattered throughout the embryo. Extensions known as vascular tubes eventually connect the vascular network. As the embryo grows within the mother’s womb, the placenta develops to supply blood rich in oxygen and nutrients via the umbilical vein and to remove wastes in oxygen-depleted blood via the umbilical arteries. Three major shunts found in the fetus are the foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus, which divert blood from the pulmonary to the systemic circuit, and the ductus venosus, which carries freshly oxygenated blood high in nutrients to the fetal heart.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?