| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The human heart is the first functional organ to develop. It begins beating and pumping blood around day 21 or 22, a mere three weeks after fertilization. This emphasizes the critical nature of the heart in distributing blood through the vessels and the vital exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and wastes both to and from the developing baby. The critical early development of the heart is reflected by the prominent heart bulge that appears on the anterior surface of the embryo.
The heart forms from an embryonic tissue called mesoderm around 18 to 19 days after fertilization. Mesoderm is one of the three primary germ layers that differentiates early in development that collectively gives rise to all subsequent tissues and organs. The heart begins to develop near the head of the embryo in a region known as the cardiogenic area . Following chemical signals called factors from the underlying endoderm (another of the three primary germ layers), the cardiogenic area begins to form two strands called the cardiogenic cords ( [link] ). As the cardiogenic cords develop, a lumen rapidly develops within them. At this point, they are referred to as endocardial tubes . The two tubes migrate together and fuse to form a single primitive heart tube . The primitive heart tube quickly forms five distinct regions. From head to tail, these include the truncus arteriosus, bulbus cordis, primitive ventricle, primitive atrium, and the sinus venosus. Initially, all venous blood flows into the sinus venosus, and contractions propel the blood from tail to head, or from the sinus venosus to the truncus arteriosus. This is a very different pattern from that of an adult.
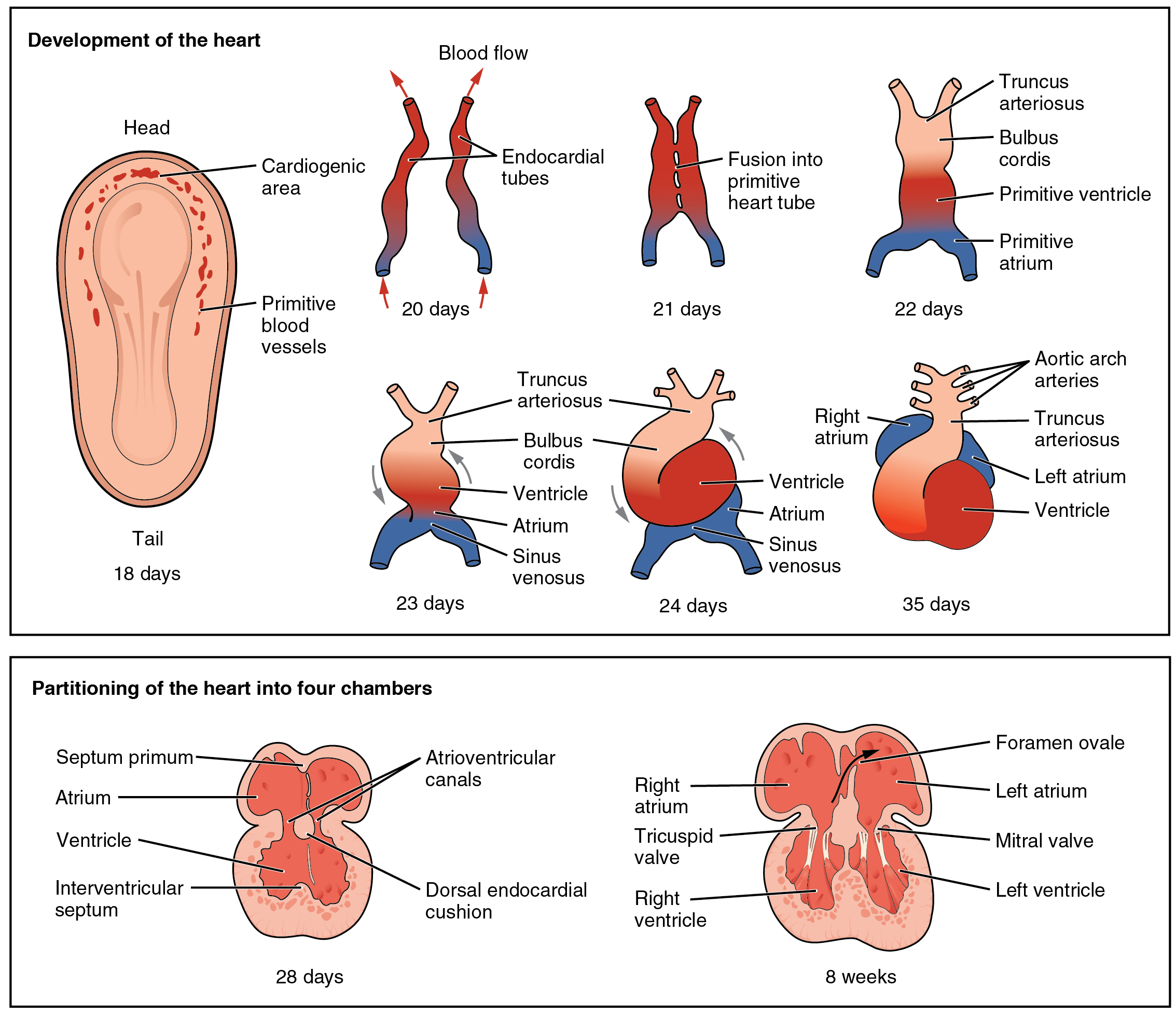
The five regions of the primitive heart tube develop into recognizable structures in a fully developed heart. The truncus arteriosus will eventually divide and give rise to the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk. The bulbus cordis develops into the right ventricle. The primitive ventricle forms the left ventricle. The primitive atrium becomes the anterior portions of both the right and left atria, and the two auricles. The sinus venosus develops into the posterior portion of the right atrium, the SA node, and the coronary sinus.
As the primitive heart tube elongates, it begins to fold within the pericardium, eventually forming an S shape, which places the chambers and major vessels into an alignment similar to the adult heart. This process occurs between days 23 and 28. The remainder of the heart development pattern includes development of septa and valves, and remodeling of the actual chambers. Partitioning of the atria and ventricles by the interatrial septum, interventricular septum, and atrioventricular septum is complete by the end of the fifth week, although the fetal blood shunts remain until birth or shortly after. The atrioventricular valves form between weeks five and eight, and the semilunar valves form between weeks five and nine.
The heart is the first organ to form and become functional, emphasizing the importance of transport of material to and from the developing infant. It originates about day 18 or 19 from the mesoderm and begins beating and pumping blood about day 21 or 22. It forms from the cardiogenic region near the head and is visible as a prominent heart bulge on the surface of the embryo. Originally, it consists of a pair of strands called cardiogenic cords that quickly form a hollow lumen and are referred to as endocardial tubes. These then fuse into a single heart tube and differentiate into the truncus arteriosus, bulbus cordis, primitive ventricle, primitive atrium, and sinus venosus, starting about day 22. The primitive heart begins to form an S shape within the pericardium between days 23 and 28. The internal septa begin to form about day 28, separating the heart into the atria and ventricles, although the foramen ovale persists until shortly after birth. Between weeks five and eight, the atrioventricular valves form. The semilunar valves form between weeks five and nine.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?