| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The hypothalamus–pituitary complex can be thought of as the “command center” of the endocrine system. This complex secretes several hormones that directly produce responses in target tissues, as well as hormones that regulate the synthesis and secretion of hormones of other glands. In addition, the hypothalamus–pituitary complex coordinates the messages of the endocrine and nervous systems. In many cases, a stimulus received by the nervous system must pass through the hypothalamus–pituitary complex to be translated into hormones that can initiate a response.
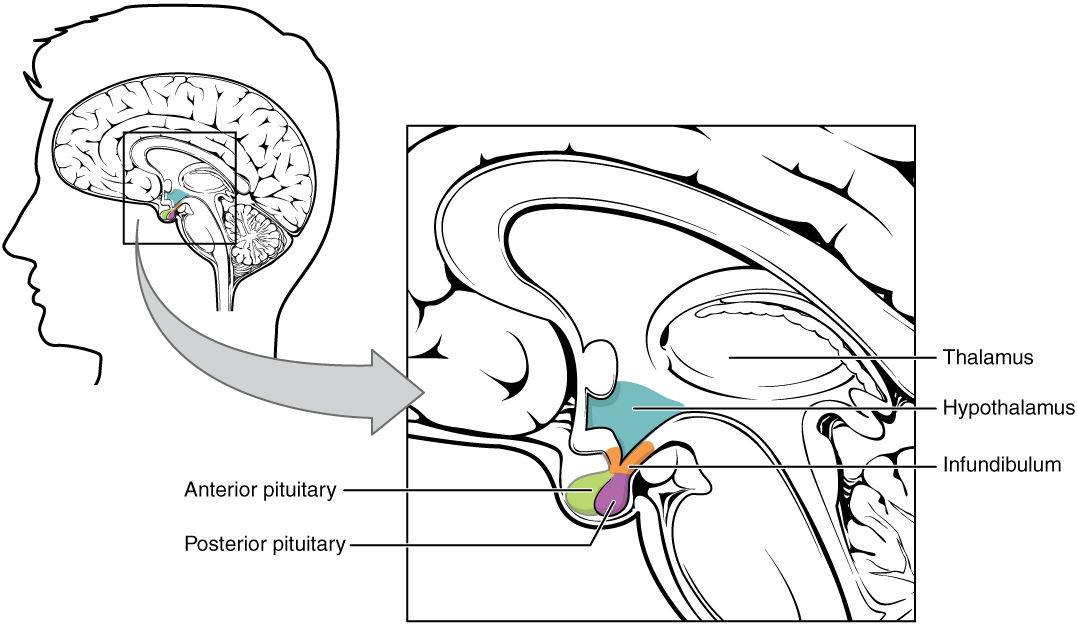
The hypothalamus is a structure of the diencephalon of the brain located anterior and inferior to the thalamus ( [link] ). It has both neural and endocrine functions, producing and secreting many hormones. In addition, the hypothalamus is anatomically and functionally related to the pituitary gland (or hypophysis), a bean-sized organ suspended from it by a stem called the infundibulum (or pituitary stalk). The pituitary gland is cradled within the sellaturcica of the sphenoid bone of the skull. It consists of two lobes that arise from distinct parts of embryonic tissue: the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) is neural tissue, whereas the anterior pituitary (also known as the adenohypophysis) is glandular tissue that develops from the primitive digestive tract. The hormones secreted by the posterior and anterior pituitary, and the intermediate zone between the lobes are summarized in [link] .
| Pituitary Hormones | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pituitary lobe | Associated hormones | Chemical class | Effect |
| Anterior | Growth hormone (GH) | Protein | Promotes growth of body tissues |
| Anterior | Prolactin (PRL) | Peptide | Promotes milk production from mammary glands |
| Anterior | Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) | Glycoprotein | Stimulates thyroid hormone release from thyroid |
| Anterior | Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Peptide | Stimulates hormone release by adrenal cortex |
| Anterior | Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) | Glycoprotein | Stimulates gamete production in gonads |
| Anterior | Luteinizing hormone (LH) | Glycoprotein | Stimulates androgen production by gonads |
| Posterior | Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) | Peptide | Stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys |
| Posterior | Oxytocin | Peptide | Stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth |
| Intermediate zone | Melanocyte-stimulating hormone | Peptide | Stimulates melanin formation in melanocytes |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?