| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The role of the cerebellum is a subject of debate. There is an obvious connection to motor function based on the clinical implications of cerebellar damage. There is also strong evidence of the cerebellar role in procedural memory. The two are not incompatible; in fact, procedural memory is motor memory, such as learning to ride a bicycle. Significant work has been performed to describe the connections within the cerebellum that result in learning. A model for this learning is classical conditioning, as shown by the famous dogs from the physiologist Ivan Pavlov’s work. This classical conditioning, which can be related to motor learning, fits with the neural connections of the cerebellum. The cerebellum is 10 percent of the mass of the brain and has varied functions that all point to a role in the motor system.
The cerebellum is located in apposition to the dorsal surface of the brain stem, centered on the pons. The name of the pons is derived from its connection to the cerebellum. The word means “bridge” and refers to the thick bundle of myelinated axons that form a bulge on its ventral surface. Those fibers are axons that project from the gray matter of the pons into the contralateral cerebellar cortex. These fibers make up the middle cerebellar peduncle (MCP) and are the major physical connection of the cerebellum to the brain stem ( [link] ). Two other white matter bundles connect the cerebellum to the other regions of the brain stem. The superior cerebellar peduncle (SCP) is the connection of the cerebellum to the midbrain and forebrain. The inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) is the connection to the medulla.
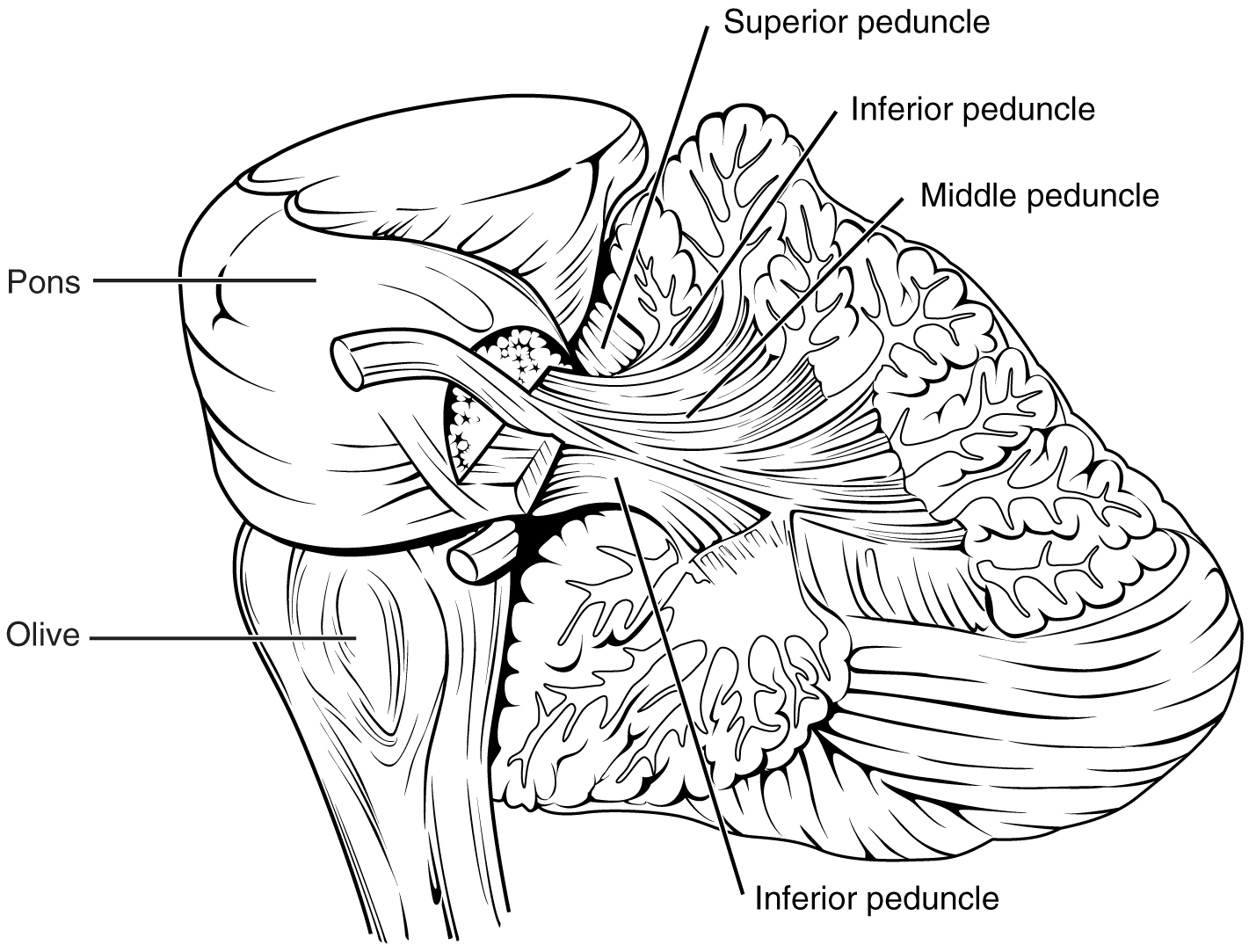
These connections can also be broadly described by their functions. The ICP conveys sensory input to the cerebellum, partially from the spinocerebellar tract, but also through fibers of the inferior olive . The MCP is part of the cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathway that connects the cerebral cortex with the cerebellum and preferentially targets the lateral regions of the cerebellum. It includes a copy of the motor commands sent from the precentral gyrus through the corticospinal tract, arising from collateral branches that synapse in the gray matter of the pons, along with input from other regions such as the visual cortex. The SCP is the major output of the cerebellum, divided between the red nucleus in the midbrain and the thalamus, which will return cerebellar processing to the motor cortex. These connections describe a circuit that compares motor commands and sensory feedback to generate a new output. These comparisons make it possible to coordinate movements. If the cerebral cortex sends a motor command to initiate walking, that command is copied by the pons and sent into the cerebellum through the MCP. Sensory feedback in the form of proprioception from the spinal cord, as well as vestibular sensations from the inner ear, enters through the ICP. If you take a step and begin to slip on the floor because it is wet, the output from the cerebellum—through the SCP—can correct for that and keep you balanced and moving. The red nucleus sends new motor commands to the spinal cord through the rubrospinal tract .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?