| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
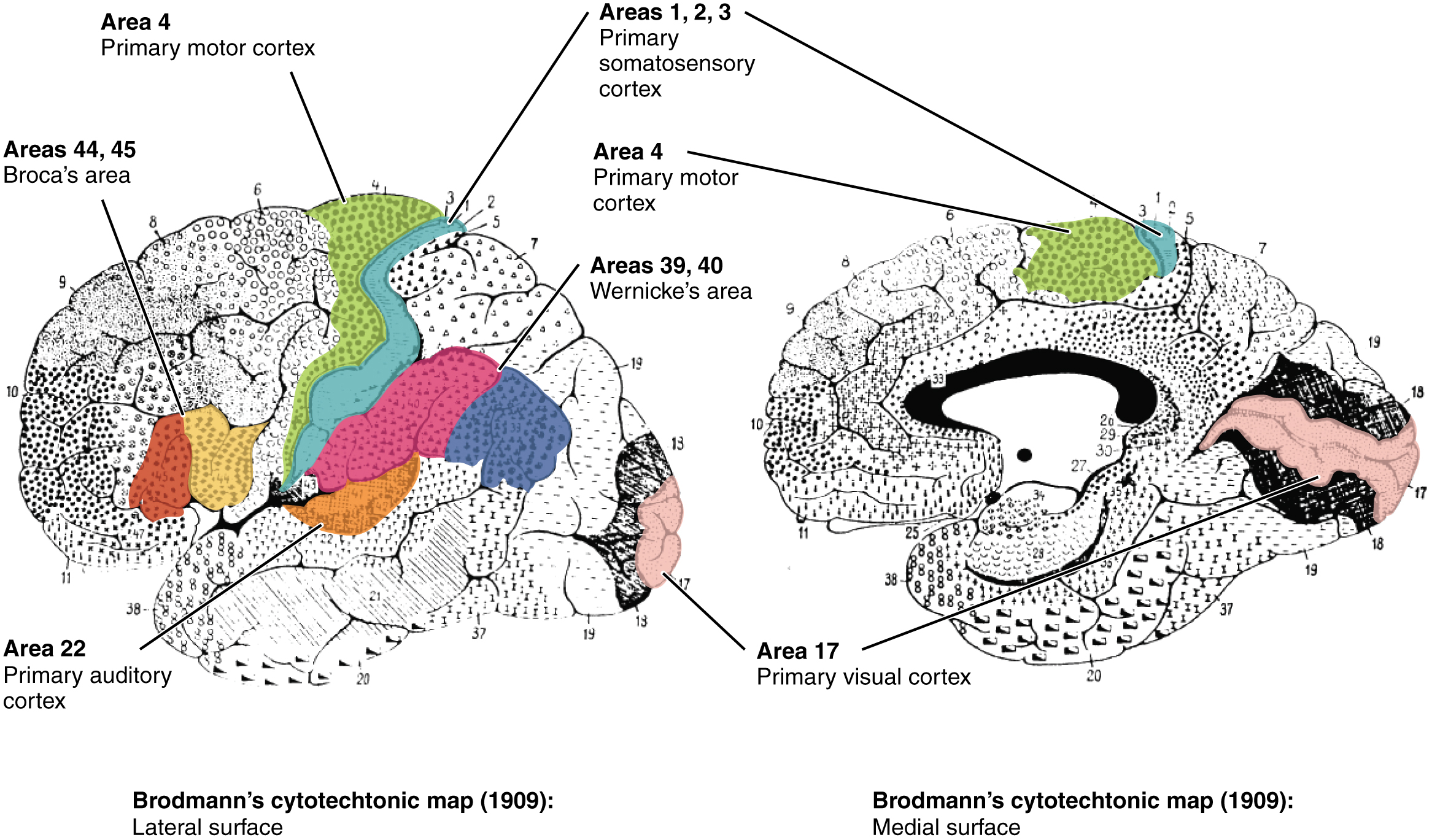
Area 17, as Brodmann described it, is also known as the primary visual cortex. Adjacent to that are areas 18 and 19, which constitute subsequent regions of visual processing. Area 22 is the primary auditory cortex, and it is followed by area 23, which further processes auditory information. Area 4 is the primary motor cortex in the precentral gyrus, whereas area 6 is the premotor cortex. These areas suggest some specialization within the cortex for functional processing, both in sensory and motor regions. The fact that Brodmann’s areas correlate so closely to functional localization in the cerebral cortex demonstrates the strong link between structure and function in these regions.
Areas 1, 2, 3, 4, 17, and 22 are each described as primary cortical areas. The adjoining regions are each referred to as association areas. Primary areas are where sensory information is initially received from the thalamus for conscious perception, or—in the case of the primary motor cortex—where descending commands are sent down to the brain stem or spinal cord to execute movements ( [link] ).
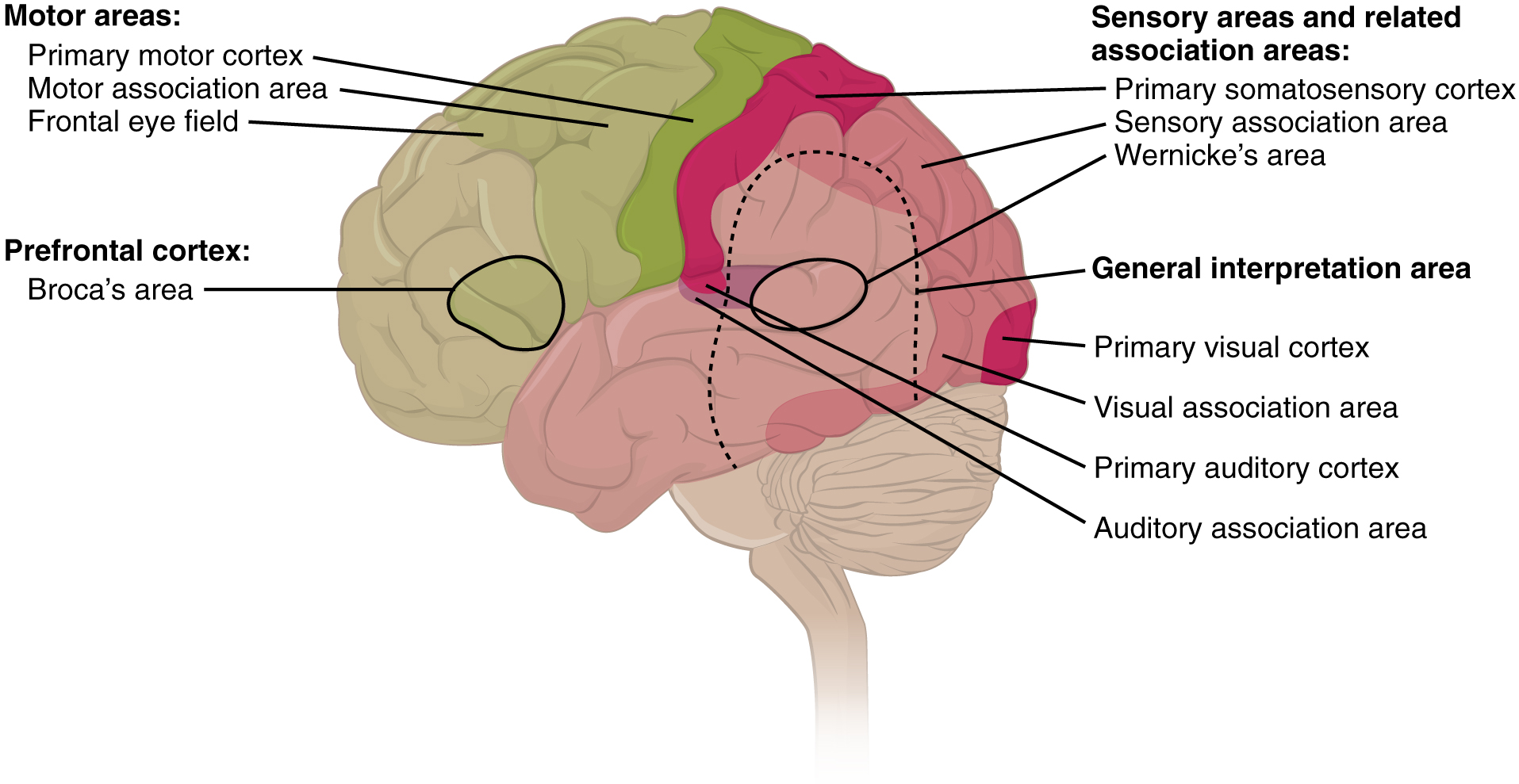
A number of other regions, which extend beyond these primary or association areas of the cortex, are referred to as integrative areas. These areas are found in the spaces between the domains for particular sensory or motor functions, and they integrate multisensory information, or process sensory or motor information in more complex ways. Consider, for example, the posterior parietal cortex that lies between the somatosensory cortex and visual cortex regions. This has been ascribed to the coordination of visual and motor functions, such as reaching to pick up a glass. The somatosensory function that would be part of this is the proprioceptive feedback from moving the arm and hand. The weight of the glass, based on what it contains, will influence how those movements are executed.
Assessment of cerebral functions is directed at cognitive abilities. The abilities assessed through the mental status exam can be separated into four groups: orientation and memory, language and speech, sensorium, and judgment and abstract reasoning.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?