| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
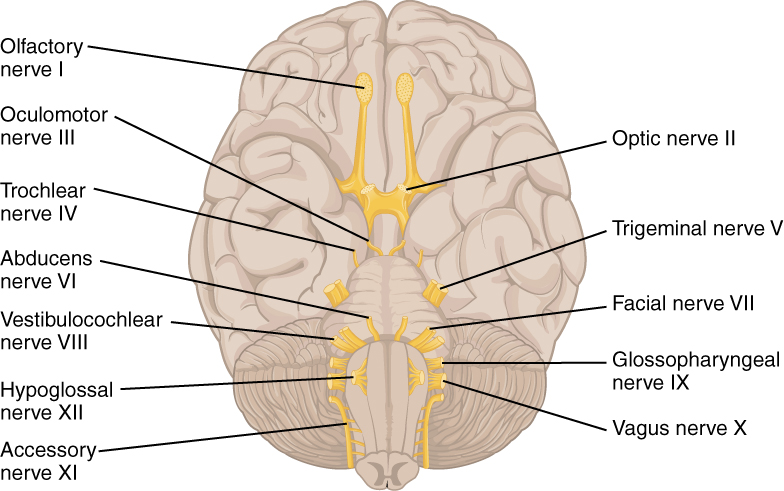
Three of the cranial nerves also contain autonomic fibers, and a fourth is almost purely a component of the autonomic system. The oculomotor, facial, and glossopharyngeal nerves contain fibers that contact autonomic ganglia. The oculomotor fibers initiate pupillary constriction, whereas the facial and glossopharyngeal fibers both initiate salivation. The vagus nerve primarily targets autonomic ganglia in the thoracic and upper abdominal cavities.
Visit this site to read about a man who wakes with a headache and a loss of vision. His regular doctor sent him to an ophthalmologist to address the vision loss. The ophthalmologist recognizes a greater problem and immediately sends him to the emergency room. Once there, the patient undergoes a large battery of tests, but a definite cause cannot be found. A specialist recognizes the problem as meningitis, but the question is what caused it originally. How can that be cured? The loss of vision comes from swelling around the optic nerve, which probably presented as a bulge on the inside of the eye. Why is swelling related to meningitis going to push on the optic nerve?
Another important aspect of the cranial nerves that lends itself to a mnemonic is the functional role each nerve plays. The nerves fall into one of three basic groups. They are sensory, motor, or both (see [link] ). The sentence, “Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Brains Beauty Matter More,” corresponds to the basic function of each nerve. The first, second, and eighth nerves are purely sensory: the olfactory (CNI), optic (CNII), and vestibulocochlear (CNVIII) nerves. The three eye-movement nerves are all motor: the oculomotor (CNIII), trochlear (CNIV), and abducens (CNVI). The spinal accessory (CNXI) and hypoglossal (CNXII) nerves are also strictly motor. The remainder of the nerves contain both sensory and motor fibers. They are the trigeminal (CNV), facial (CNVII), glossopharyngeal (CNIX), and vagus (CNX) nerves. The nerves that convey both are often related to each other. The trigeminal and facial nerves both concern the face; one concerns the sensations and the other concerns the muscle movements. The facial and glossopharyngeal nerves are both responsible for conveying gustatory, or taste, sensations as well as controlling salivary glands. The vagus nerve is involved in visceral responses to taste, namely the gag reflex. This is not an exhaustive list of what these combination nerves do, but there is a thread of relation between them.
| Cranial Nerves | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mnemonic | # | Name | Function (S/M/B) | Central connection (nuclei) | Peripheral connection (ganglion or muscle) |
| On | I | Olfactory | Smell (S) | Olfactory bulb | Olfactory epithelium |
| Old | II | Optic | Vision (S) | Hypothalamus/thalamus/midbrain | Retina (retinal ganglion cells) |
| Olympus’ | III | Oculomotor | Eye movements (M) | Oculomotor nucleus | Extraocular muscles (other 4), levator palpebrae superioris, ciliary ganglion (autonomic) |
| Towering | IV | Trochlear | Eye movements (M) | Trochlear nucleus | Superior oblique muscle |
| Tops | V | Trigeminal | Sensory/motor – face (B) | Trigeminal nuclei in the midbrain, pons, and medulla | Trigeminal |
| A | VI | Abducens | Eye movements (M) | Abducens nucleus | Lateral rectus muscle |
| Finn | VII | Facial | Motor – face, Taste (B) | Facial nucleus, solitary nucleus, superior salivatory nucleus | Facial muscles, Geniculate ganglion, Pterygopalatine ganglion (autonomic) |
| And | VIII | Auditory (Vestibulocochlear) | Hearing/balance (S) | Cochlear nucleus, Vestibular nucleus/cerebellum | Spiral ganglion (hearing), Vestibular ganglion (balance) |
| German | IX | Glossopharyngeal | Motor – throat Taste (B) | Solitary nucleus, inferior salivatory nucleus, nucleus ambiguus | Pharyngeal muscles, Geniculate ganglion, Otic ganglion (autonomic) |
| Viewed | X | Vagus | Motor/sensory – viscera (autonomic) (B) | Medulla | Terminal ganglia serving thoracic and upper abdominal organs (heart and small intestines) |
| Some | XI | Spinal Accessory | Motor – head and neck (M) | Spinal accessory nucleus | Neck muscles |
| Hops | XII | Hypoglossal | Motor – lower throat (M) | Hypoglossal nucleus | Muscles of the larynx and lower pharynx |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?