| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts the depolarization, but the action potential runs on its own once a threshold has been reached. The question is now, “What flips the light switch on?” Temporary changes to the cell membrane voltage can result from neurons receiving information from the environment, or from the action of one neuron on another. These special types of potentials influence a neuron and determine whether an action potential will occur or not. Many of these transient signals originate at the synapse.
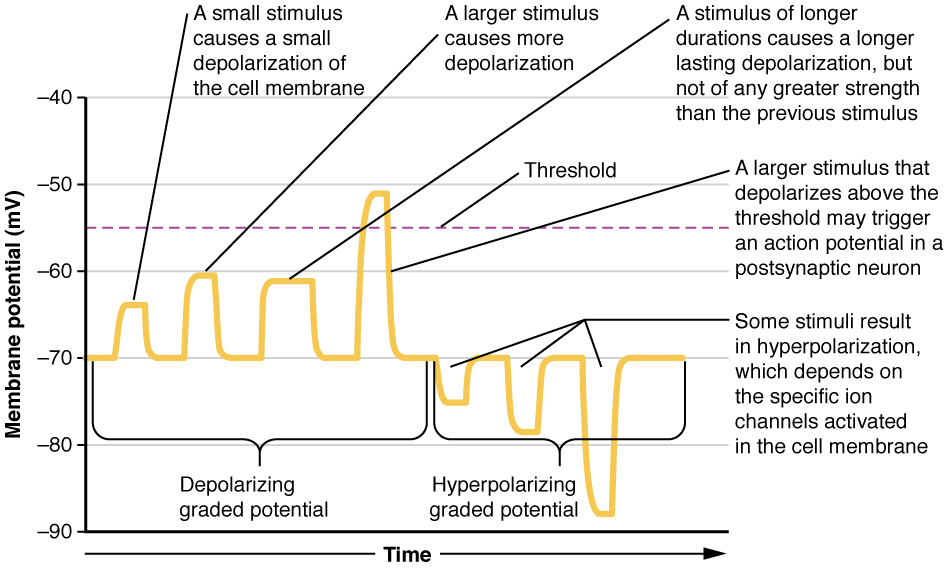
Local changes in the membrane potential are called graded potentials and are usually associated with the dendrites of a neuron. The amount of change in the membrane potential is determined by the size of the stimulus that causes it. In the example of testing the temperature of the shower, slightly warm water would only initiate a small change in a thermoreceptor, whereas hot water would cause a large amount of change in the membrane potential.
Graded potentials can be of two sorts, either they are depolarizing or hyperpolarizing ( [link] ). For a membrane at the resting potential, a graded potential represents a change in that voltage either above -70 mV or below -70 mV. Depolarizing graded potentials are often the result of Na + or Ca 2+ entering the cell. Both of these ions have higher concentrations outside the cell than inside; because they have a positive charge, they will move into the cell causing it to become less negative relative to the outside. Hyperpolarizing graded potentials can be caused by K + leaving the cell or Cl - entering the cell. If a positive charge moves out of a cell, the cell becomes more negative; if a negative charge enters the cell, the same thing happens.
For the unipolar cells of sensory neurons—both those with free nerve endings and those within encapsulations—graded potentials develop in the dendrites that influence the generation of an action potential in the axon of the same cell. This is called a generator potential . For other sensory receptor cells, such as taste cells or photoreceptors of the retina, graded potentials in their membranes result in the release of neurotransmitters at synapses with sensory neurons. This is called a receptor potential .
A postsynaptic potential (PSP) is the graded potential in the dendrites of a neuron that is receiving synapses from other cells. Postsynaptic potentials can be depolarizing or hyperpolarizing. Depolarization in a postsynaptic potential is called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) because it causes the membrane potential to move toward threshold. Hyperpolarization in a postsynaptic potential is an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) because it causes the membrane potential to move away from threshold.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?