| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The functions of the nervous system—sensation, integration, and response—depend on the functions of the neurons underlying these pathways. To understand how neurons are able to communicate, it is necessary to describe the role of an excitable membrane in generating these signals. The basis of this communication is the action potential, which demonstrates how changes in the membrane can constitute a signal. Looking at the way these signals work in more variable circumstances involves a look at graded potentials, which will be covered in the next section.
Most cells in the body make use of charged particles, ions, to build up a charge across the cell membrane. Previously, this was shown to be a part of how muscle cells work. For skeletal muscles to contract, based on excitation–contraction coupling, requires input from a neuron. Both of the cells make use of the cell membrane to regulate ion movement between the extracellular fluid and cytosol.
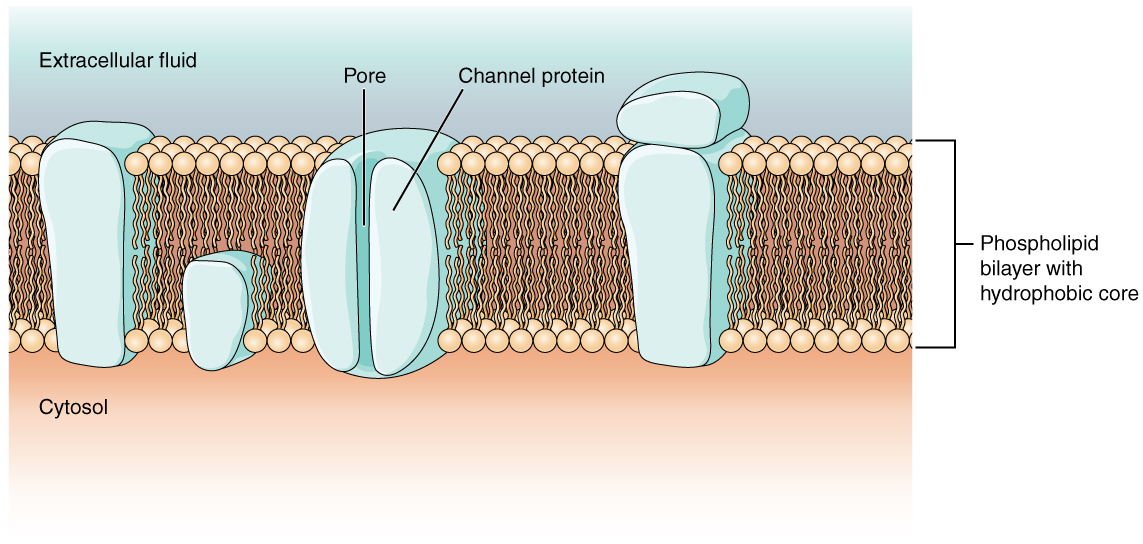
As you learned in the chapter on cells, the cell membrane is primarily responsible for regulating what can cross the membrane and what stays on only one side. The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer, so only substances that can pass directly through the hydrophobic core can diffuse through unaided. Charged particles, which are hydrophilic by definition, cannot pass through the cell membrane without assistance ( [link] ). Transmembrane proteins, specifically channel proteins, make this possible. Several passive transport channels, as well as active transport pumps, are necessary to generate a transmembrane potential and an action potential. Of special interest is the carrier protein referred to as the sodium/potassium pump that moves sodium ions (Na + ) out of a cell and potassium ions (K + ) into a cell, thus regulating ion concentration on both sides of the cell membrane.
The sodium/potassium pump requires energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), so it is also referred to as an ATPase. As was explained in the cell chapter, the concentration of Na + is higher outside the cell than inside, and the concentration of K + is higher inside the cell than outside. That means that this pump is moving the ions against the concentration gradients for sodium and potassium, which is why it requires energy. In fact, the pump basically maintains those concentration gradients.
Ion channels are pores that allow specific charged particles to cross the membrane in response to an existing concentration gradient. Proteins are capable of spanning the cell membrane, including its hydrophobic core, and can interact with the charge of ions because of the varied properties of amino acids found within specific domains or regions of the protein channel. Hydrophobic amino acids are found in the domains that are apposed to the hydrocarbon tails of the phospholipids. Hydrophilic amino acids are exposed to the fluid environments of the extracellular fluid and cytosol. Additionally, the ions will interact with the hydrophilic amino acids, which will be selective for the charge of the ion. Channels for cations (positive ions) will have negatively charged side chains in the pore. Channels for anions (negative ions) will have positively charged side chains in the pore. This is called electrochemical exclusion , meaning that the channel pore is charge-specific.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?