| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The appendicular muscles of the lower body position and stabilize the pelvic girdle , which serves as a foundation for the lower limbs. Comparatively, there is much more movement at the pectoral girdle than at the pelvic girdle. There is very little movement of the pelvic girdle because of its connection with the sacrum at the base of the axial skeleton. The pelvic girdle is less range of motion because it was designed to stabilize and support the body.
What would happen if the pelvic girdle, which attaches the lower limbs to the torso, were capable of the same range of motion as the pectoral girdle? For one thing, walking would expend more energy if the heads of the femurs were not secured in the acetabula of the pelvis. The body’s center of gravity is in the area of the pelvis. If the center of gravity were not to remain fixed, standing up would be difficult as well. Therefore, what the leg muscles lack in range of motion and versatility, they make up for in size and power, facilitating the body’s stabilization, posture, and movement.
Most muscles that insert on the femur (the thigh bone) and move it, originate on the pelvic girdle. The psoas major and iliacus make up the iliopsoas group . Some of the largest and most powerful muscles in the body are the gluteal muscles or gluteal group . The gluteus maximus is the largest; deep to the gluteus maximus is the gluteus medius , and deep to the gluteus medius is the gluteus minimus , the smallest of the trio ( [link] and [link] ).

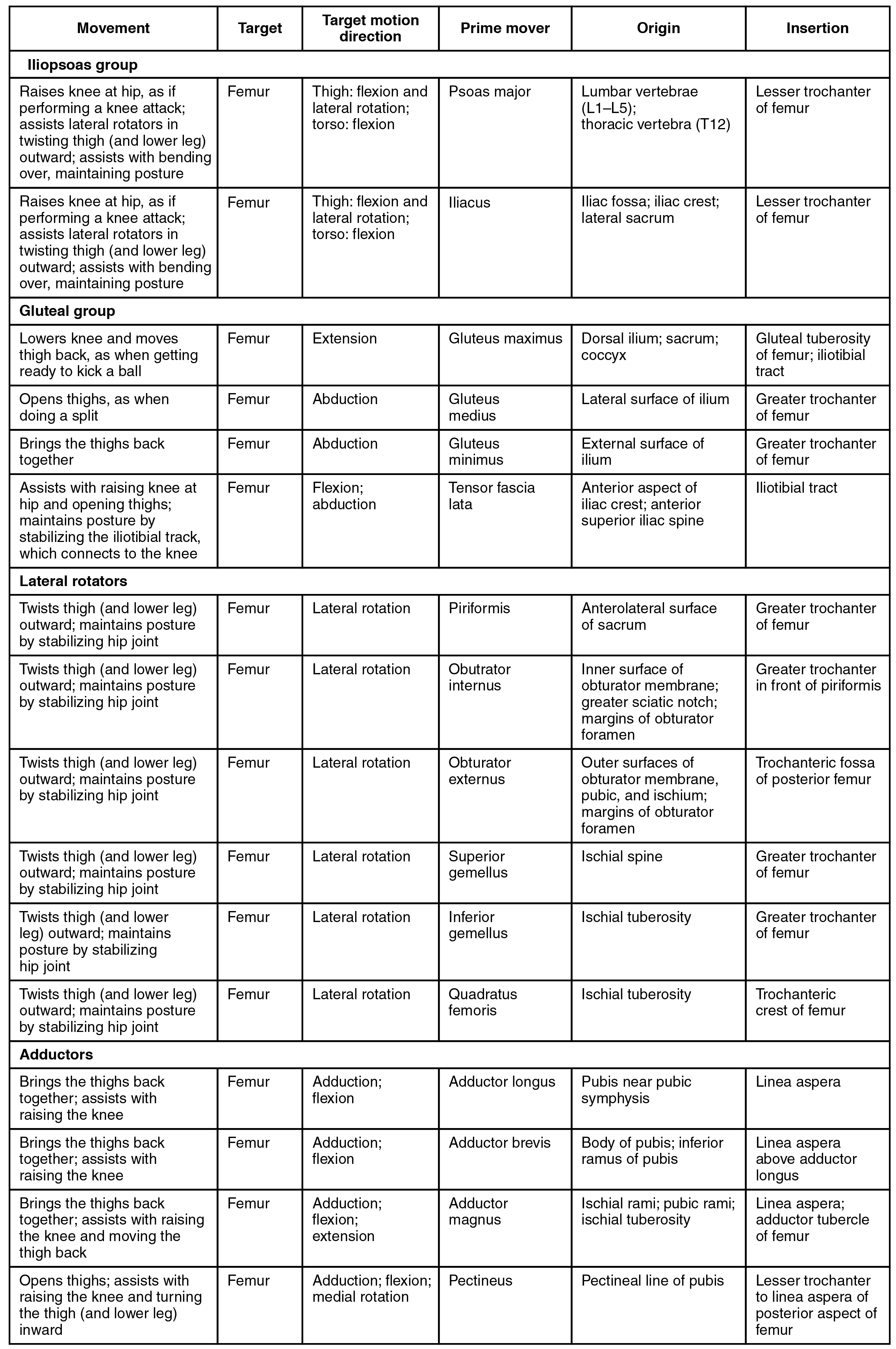
The tensor fascia latae is a thick, squarish muscle in the superior aspect of the lateral thigh. It acts as a synergist of the gluteus medius and iliopsoas in flexing and abducting the thigh. It also helps stabilize the lateral aspect of the knee by pulling on the iliotibial tract (band), making it taut. Deep to the gluteus maximus, the piriformis , obturator internus , obturator externus , superior gemellus , inferior gemellus , and quadratus femoris laterally rotate the femur at the hip.
The adductor longus , adductor brevis , and adductor magnus can both medially and laterally rotate the thigh depending on the placement of the foot. The adductor longus flexes the thigh, whereas the adductor magnus extends it. The pectineus adducts and flexes the femur at the hip as well. The pectineus is located in the femoral triangle , which is formed at the junction between the hip and the leg and also includes the femoral nerve, the femoral artery, the femoral vein, and the deep inguinal lymph nodes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?