| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
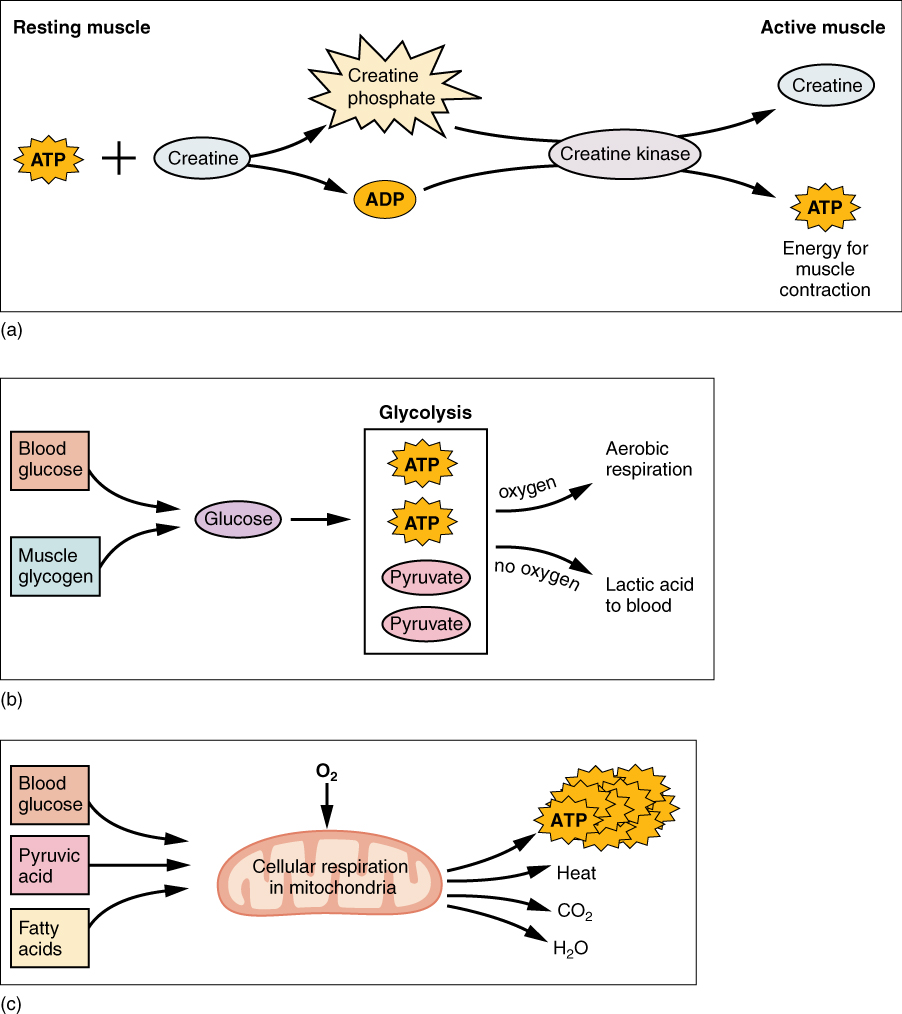
As the ATP produced by creatine phosphate is depleted, muscles turn to glycolysis as an ATP source. Glycolysis is an anaerobic (non-oxygen-dependent) process that breaks down glucose (sugar) to produce ATP; however, glycolysis cannot generate ATP as quickly as creatine phosphate. Thus, the switch to glycolysis results in a slower rate of ATP availability to the muscle. The sugar used in glycolysis can be provided by blood glucose or by metabolizing glycogen that is stored in the muscle. The breakdown of one glucose molecule produces two ATP and two molecules of pyruvic acid , which can be used in aerobic respiration or when oxygen levels are low, converted to lactic acid ( [link] b ).
If oxygen is available, pyruvic acid is used in aerobic respiration. However, if oxygen is not available, pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid , which may contribute to muscle fatigue. This conversion allows the recycling of the enzyme NAD + from NADH, which is needed for glycolysis to continue. This occurs during strenuous exercise when high amounts of energy are needed but oxygen cannot be sufficiently delivered to muscle. Glycolysis itself cannot be sustained for very long (approximately 1 minute of muscle activity), but it is useful in facilitating short bursts of high-intensity output. This is because glycolysis does not utilize glucose very efficiently, producing a net gain of two ATPs per molecule of glucose, and the end product of lactic acid, which may contribute to muscle fatigue as it accumulates.
Aerobic respiration is the breakdown of glucose or other nutrients in the presence of oxygen (O 2 ) to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Approximately 95 percent of the ATP required for resting or moderately active muscles is provided by aerobic respiration, which takes place in mitochondria. The inputs for aerobic respiration include glucose circulating in the bloodstream, pyruvic acid, and fatty acids. Aerobic respiration is much more efficient than anaerobic glycolysis, producing approximately 36 ATPs per molecule of glucose versus four from glycolysis. However, aerobic respiration cannot be sustained without a steady supply of O 2 to the skeletal muscle and is much slower ( [link] c ). To compensate, muscles store small amount of excess oxygen in proteins call myoglobin, allowing for more efficient muscle contractions and less fatigue. Aerobic training also increases the efficiency of the circulatory system so that O 2 can be supplied to the muscles for longer periods of time.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?