| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The sequence of events that result in the contraction of an individual muscle fiber begins with a signal—the neurotransmitter, ACh—from the motor neuron innervating that fiber. The local membrane of the fiber will depolarize as positively charged sodium ions (Na + ) enter, triggering an action potential that spreads to the rest of the membrane will depolarize, including the T-tubules. This triggers the release of calcium ions (Ca ++ ) from storage in the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). The Ca ++ then initiates contraction, which is sustained by ATP ( [link] ). As long as Ca ++ ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin, which keeps the actin-binding sites “unshielded,” and as long as ATP is available to drive the cross-bridge cycling and the pulling of actin strands by myosin, the muscle fiber will continue to shorten to an anatomical limit.
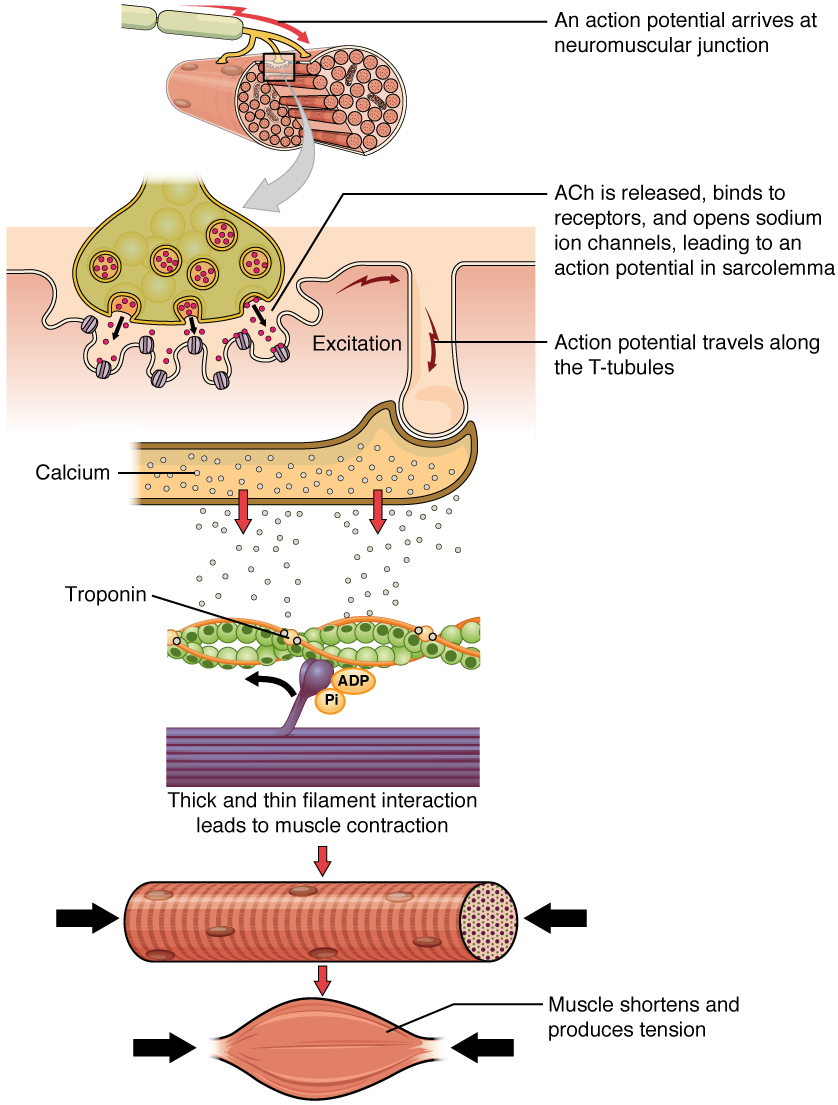
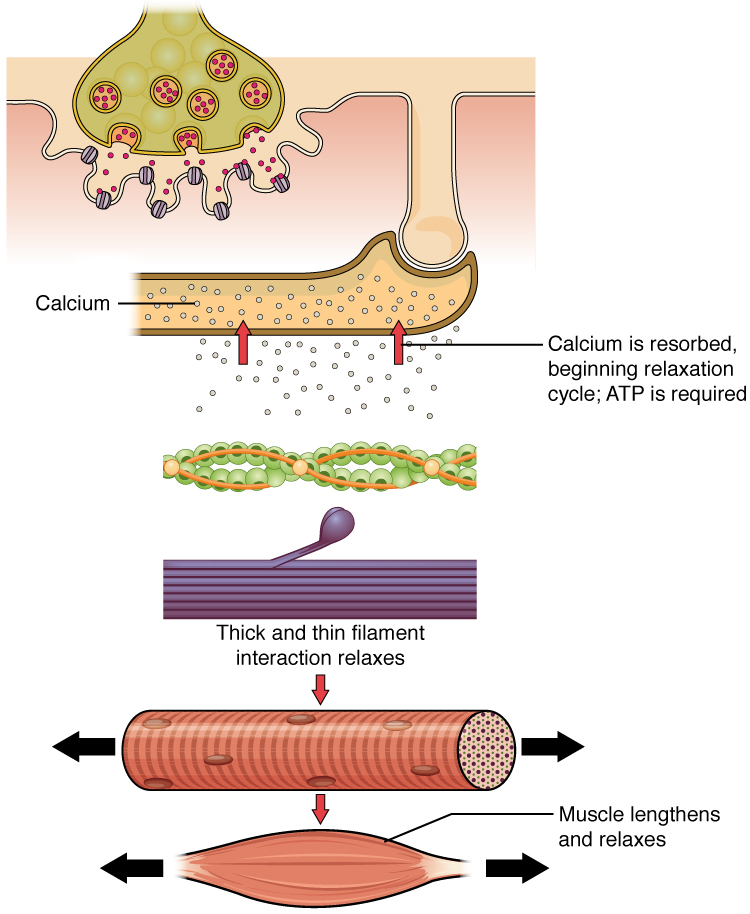
Muscle contraction usually stops when signaling from the motor neuron ends, which repolarizes the sarcolemma and T-tubules, and closes the voltage-gated calcium channels in the SR. Ca ++ ions are then pumped back into the SR, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield (or re-cover) the binding sites on the actin strands. A muscle also can stop contracting when it runs out of ATP and becomes fatigued ( [link] ).
The release of calcium ions initiates muscle contractions. Watch this video to learn more about the role of calcium. (a) What are “T-tubules” and what is their role? (b) Please describe how actin-binding sites are made available for cross-bridging with myosin heads during contraction.
The molecular events of muscle fiber shortening occur within the fiber’s sarcomeres (see [link] ). The contraction of a striated muscle fiber occurs as the sarcomeres, linearly arranged within myofibrils, shorten as myosin heads pull on the actin filaments.
The region where thick and thin filaments overlap has a dense appearance, as there is little space between the filaments. This zone where thin and thick filaments overlap is very important to muscle contraction, as it is the site where filament movement starts. Thin filaments, anchored at their ends by the Z-discs, do not extend completely into the central region that only contains thick filaments, anchored at their bases at a spot called the M-line. A myofibril is composed of many sarcomeres running along its length; thus, myofibrils and muscle cells contract as the sarcomeres contract.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?