| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Factor completely: .
| Is there a GCF? | No. |
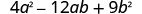 |
| Is it a binomial, trinomial, or are there
more terms? |
||
| Trinomial with
. But the first term is a
perfect square. |
||
| Is the last term a perfect square? | Yes. |
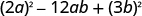 |
| Does it fit the pattern, | Yes. |
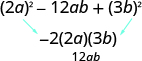 |
| Write it as a square. |
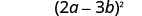 | |
| Check your answer. | ||
| Is the expression factored completely? | ||
| Yes. | ||
| The binomial is not a difference of squares. | ||
| Multiply. | ||
Factor completely: .
| Is there a GCF? | Yes, 3. | |
| Factor it out. | ||
| In the parentheses, is it a binomial, trinomial,
or are there more than three terms? |
Binomial. | |
| Is it a sum or difference? | Sum. | |
| Of squares or cubes? | Sum of cubes. |
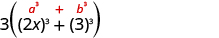 |
| Write it using the sum of cubes pattern. |
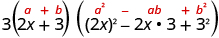 | |
| Is the expression factored completely? | Yes. | |
| Check by multiplying. | We leave the check to you. |
Recognize and Use the Appropriate Method to Factor a Polynomial Completely
In the following exercises, factor completely.
Watermelon drop A springtime tradition at the University of California San Diego is the Watermelon Drop, where a watermelon is dropped from the seventh story of Urey Hall.
ⓐ ⓑ
Pumpkin drop A fall tradition at the University of California San Diego is the Pumpkin Drop, where a pumpkin is dropped from the eleventh story of Tioga Hall.
The difference of squares can be factored as . But it is not completely factored. What more must be done to completely factor it?
Of all the factoring methods covered in this chapter (GCF, grouping, undo FOIL, ‘ac’ method, special products) which is the easiest for you? Which is the hardest? Explain your answers.
ⓐ After completing the exercises, use this checklist to evaluate your mastery of the objectives of this section.
ⓑ Overall, after looking at the checklist, do you think you are well-prepared for the next section? Why or why not?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?