| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
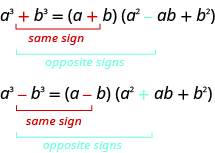
The two patterns look very similar, don’t they? But notice the signs in the factors. The sign of the binomial factor matches the sign in the original binomial. And the sign of the middle term of the trinomial factor is the opposite of the sign in the original binomial. If you recognize the pattern of the signs, it may help you memorize the patterns.
The trinomial factor in the sum and difference of cubes pattern cannot be factored.
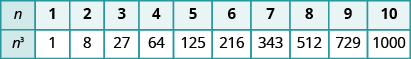
It can be very helpful if you learn to recognize the cubes of the integers from 1 to 10, just like you have learned to recognize squares. We have listed the cubes of the integers from 1 to 10 in [link] .
To factor the sum or difference of cubes:
Factor: .
 | |
| This binomial is a difference. The first and last terms are perfect cubes. | |
| Write the terms as cubes. |
 |
| Use the difference of cubes pattern. |
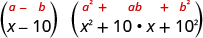 |
| Simplify. |
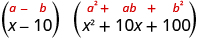 |
| Check by multiplying. | |
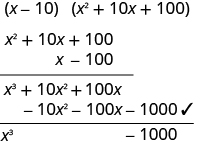 |
Be careful to use the correct signs in the factors of the sum and difference of cubes.
Factor: .
 | |
| This binomial is a difference. The first and last terms are perfect cubes. | |
| Write the terms as cubes. |
 |
| Use the difference of cubes pattern. |
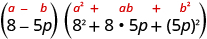 |
| Simplify. |
 |
| Check by multiplying. | We'll leave the check to you. |
Factor: .
 | |
| This binomial is a difference. The first and last terms are perfect cubes. | |
| Write the terms as cubes. |
 |
| Use the difference of cubes pattern. |
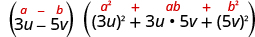 |
| Simplify. |
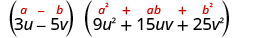 |
| Check by multiplying. | We'll leave the check to you. |
In the next example, we first factor out the GCF. Then we can recognize the sum of cubes.
Factor: .
 | |
| Factor the common factor. |
 |
| This binomial is a sum. The first and last terms are perfect cubes. | |
| Write the terms as cubes. |
 |
| Use the sum of cubes pattern. |
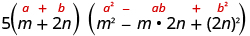 |
| Simplify. |
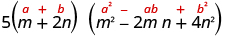 |
Check. To check, you may find it easier to multiply the sum of cubes factors first, then multiply that product by 5. We’ll leave the multiplication for you.
Access these online resources for additional instruction and practice with factoring special products.
Factor Perfect Square Trinomials
In the following exercises, factor.
Factor Differences of Squares
In the following exercises, factor.
Factor Sums and Differences of Cubes
In the following exercises, factor.
Mixed Practice
In the following exercises, factor.
Landscaping Sue and Alan are planning to put a 15 foot square swimming pool in their backyard. They will surround the pool with a tiled deck, the same width on all sides. If the width of the deck is w , the total area of the pool and deck is given by the trinomial . Factor the trinomial.
Home repair The height a twelve foot ladder can reach up the side of a building if the ladder’s base is b feet from the building is the square root of the binomial . Factor the binomial.
Why was it important to practice using the binomial squares pattern in the chapter on multiplying polynomials?
Answers may vary.
How do you recognize the binomial squares pattern?
Explain why . Use algebra, words, or pictures.
Answers may vary.
Maribel factored as . Was she right or wrong? How do you know?
ⓐ After completing the exercises, use this checklist to evaluate your mastery of the objectives of this section.
ⓑ On a scale of 1–10, how would you rate your mastery of this section in light of your responses on the checklist? How can you improve this?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?