| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We can extend the Product Property for Exponents to more than two factors.
Simplify:
 | |
| Add the exponents, since bases are the same. |
 |
| Simplify. |
 |
Now let’s look at an exponential expression that contains a power raised to a power. See if you can discover a general property.
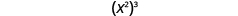 | |
| What does this mean?
How many factors altogether? |
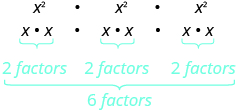 |
| So we have |
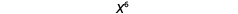 |
| Notice that 6 is the product of the exponents, 2 and 3. |
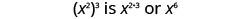 |
We write:
We multiplied the exponents. This leads to the Power Property for Exponents.
If is a real number, and are whole numbers, then
To raise a power to a power, multiply the exponents.
An example with numbers helps to verify this property.
Simplify: ⓐ ⓑ
ⓐ
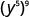 | |
| Use the power property, ( a m ) n = a m·n . |
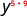 |
| Simplify. |
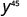 |
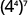 | |
| Use the power property. |
 |
| Simplify. |
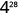 |
We will now look at an expression containing a product that is raised to a power. Can you find this pattern?
Notice that each factor was raised to the power and is .
The exponent applies to each of the factors! This leads to the Product to a Power Property for Exponents.
If and are real numbers and is a whole number, then
To raise a product to a power, raise each factor to that power.
An example with numbers helps to verify this property:
Simplify: ⓐ ⓑ
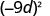 | |
| Use Power of a Product Property, ( ab ) m = a m b m . |
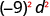 |
| Simplify. |
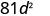 |
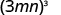 | |
| Use Power of a Product Property, ( ab ) m = a m b m . |
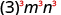 |
| Simplify. |
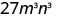 |
We now have three properties for multiplying expressions with exponents. Let’s summarize them and then we’ll do some examples that use more than one of the properties.
If are real numbers, and are whole numbers, then
All exponent properties hold true for any real numbers . Right now, we only use whole number exponents.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?