| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When an expression does not appear to have like radicals, we will simplify each radical first. Sometimes this leads to an expression with like radicals.
Access these online resources for additional instruction and practice with simplifying higher roots.
Simplify Expressions with Higher Roots
In the following exercises, simplify.
Use the Product Property to Simplify Expressions with Higher Roots
In the following exercises, simplify.
Use the Quotient Property to Simplify Expressions with Higher Roots
In the following exercises, simplify.
Add and Subtract Higher Roots
In the following exercises, simplify.
Mixed Practice
In the following exercises, simplify.
Population growth The expression models the growth of a mold population after generations. There were 10 spores at the start, and each had offspring. So is the number of offspring at the fifth generation. At the fifth generation there were 10,240 offspring. Simplify the expression to determine the number of offspring of each spore.
Spread of a virus The expression models the spread of a virus after cycles. There were three people originally infected with the virus, and each of them infected people. So is the number of people infected on the fourth cycle. At the fourth cycle 1875 people were infected. Simplify the expression to determine the number of people each person infected.
Explain how you know that .
ⓐ After completing the exercises, use this checklist to evaluate your mastery of the objectives of this section.
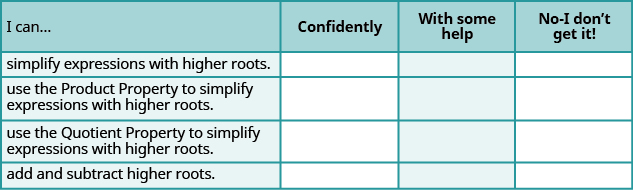
ⓑ What does this checklist tell you about your mastery of this section? What steps will you take to improve?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?