| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Some students find it helpful to draw in arrows to remind them how to use the distributive property. Then the first step in [link] would look like this:

Using the distributive property as shown in [link] will be very useful when we solve money applications in later chapters.
When we distribute a negative number, we need to be extra careful to get the signs correct!
Simplify:
| Distribute. |
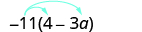 |
| Multiply. |
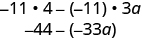 |
| Simplify. |
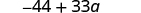 |
Notice that you could also write the result as Do you know why?
[link] will show how to use the distributive property to find the opposite of an expression.
There will be times when we’ll need to use the distributive property as part of the order of operations. Start by looking at the parentheses. If the expression inside the parentheses cannot be simplified, the next step would be multiply using the distributive property, which removes the parentheses. The next two examples will illustrate this.
Simplify:
Be sure to follow the order of operations. Multiplication comes before subtraction, so we will distribute the 2 first and then subtract.
All the properties of real numbers we have used in this chapter are summarized in [link] .
| Commutative Property | |
|
of addition If
are real numbers, then
of multiplication If are real numbers, then |
|
| Associative Property | |
|
of addition If
are real numbers, then
of multiplication If are real numbers, then |
|
| Distributive Property | |
| If are real numbers, then | |
| Identity Property | |
|
of addition For any real number
0 is the additive identity of multiplication For any real number is the multiplicative identity |
|
| Inverse Property | |
|
of addition For any real number
is the additive inverse of of multiplication For any real number is the multiplicative inverse of |
|
| Properties of Zero | |
| For any real number
a ,
For any real number For any real number |
is undefined |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?