| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A more thorough introduction to the topics covered in this section can be found in the Prealgebra chapter, Integers .
Since multiplication is mathematical shorthand for repeated addition, our model can easily be applied to show multiplication of integers . Let’s look at this concrete model to see what patterns we notice. We will use the same examples that we used for addition and subtraction. Here, we will use the model just to help us discover the pattern.
We remember that means add a , b times. Here, we are using the model just to help us discover the pattern.
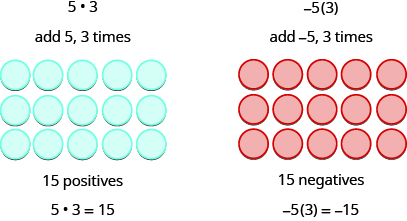
The next two examples are more interesting.
What does it mean to multiply 5 by It means subtract 5, 3 times. Looking at subtraction as “taking away,” it means to take away 5, 3 times. But there is nothing to take away, so we start by adding neutral pairs on the workspace. Then we take away 5 three times.
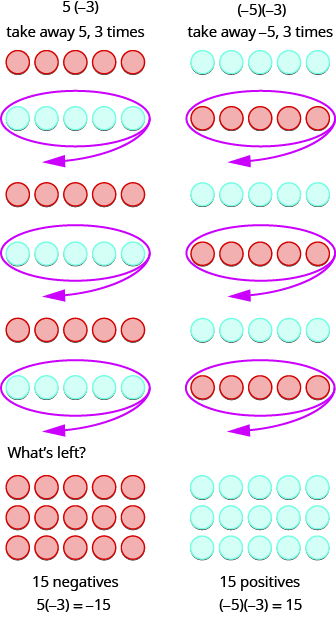
In summary:
Notice that for multiplication of two signed numbers, when the:
We’ll put this all together in the chart below.
For multiplication of two signed numbers:
| Same signs | Product | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Two positives
Two negatives |
Positive
Positive |
| Different signs | Product | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive · negative
Negative · positive |
Negative
Negative |
When we multiply a number by 1, the result is the same number. What happens when we multiply a number by Let’s multiply a positive number and then a negative number by to see what we get.
Each time we multiply a number by we get its opposite!
Multiplying a number by gives its opposite.
What about division ? Division is the inverse operation of multiplication. So, because In words, this expression says that 15 can be divided into three groups of five each because adding five three times gives 15. Look at some examples of multiplying integers, to figure out the rules for dividing integers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?