| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
The strategy for factoring we developed in the last section will guide you as you factor most binomials, trinomials, and polynomials with more than three terms. We have seen that some binomials and trinomials result from special products—squaring binomials and multiplying conjugates. If you learn to recognize these kinds of polynomials, you can use the special products patterns to factor them much more quickly.
Some trinomials are perfect squares. They result from multiplying a binomial times itself. You can square a binomial by using FOIL, but using the Binomial Squares pattern you saw in a previous chapter saves you a step. Let’s review the Binomial Squares pattern by squaring a binomial using FOIL.
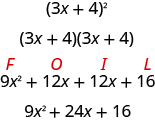
The first term is the square of the first term of the binomial and the last term is the square of the last. The middle term is twice the product of the two terms of the binomial.
The trinomial 9 x 2 + 24 +16 is called a perfect square trinomial. It is the square of the binomial 3 x +4.
We’ll repeat the Binomial Squares Pattern here to use as a reference in factoring.
If a and b are real numbers,
When you square a binomial, the product is a perfect square trinomial. In this chapter, you are learning to factor—now, you will start with a perfect square trinomial and factor it into its prime factors.
You could factor this trinomial using the methods described in the last section, since it is of the form ax 2 + bx + c . But if you recognize that the first and last terms are squares and the trinomial fits the perfect square trinomials pattern , you will save yourself a lot of work.
Here is the pattern—the reverse of the binomial squares pattern.
If a and b are real numbers,
To make use of this pattern, you have to recognize that a given trinomial fits it. Check first to see if the leading coefficient is a perfect square, . Next check that the last term is a perfect square, . Then check the middle term—is it twice the product, 2 ab ? If everything checks, you can easily write the factors.
The sign of the middle term determines which pattern we will use. When the middle term is negative, we use the pattern , which factors to .
The steps are summarized here.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?