| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Let’s look at .
| Distibutive Property | FOIL |
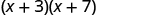 |
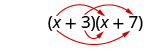 |
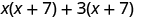 |
|
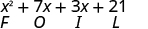 |
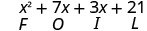 |
 |
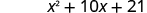 |
Notice how the terms in third line fit the FOIL pattern.
Now we will do an example where we use the FOIL pattern to multiply two binomials.
We summarize the steps of the FOIL method below. The FOIL method only applies to multiplying binomials, not other polynomials!
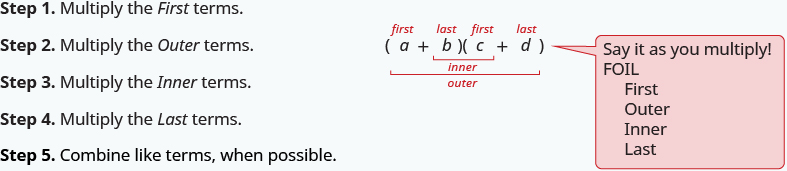
When you multiply by the FOIL method, drawing the lines will help your brain focus on the pattern and make it easier to apply.
The final products in the last four examples were trinomials because we could combine the two middle terms. This is not always the case.
Multiply:
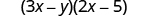 | |
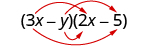 | |
| Multiply the First . |
 |
| Multiply the Outer . |
 |
| Multiply the Inner . |
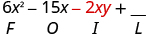 |
| Multiply the Last . |
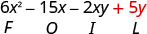 |
| Combine like terms—there are none. |
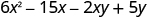 |
Be careful of the exponents in the next example.
Multiply:
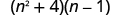 | |
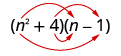 | |
| Multiply the First . |
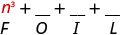 |
| Multiply the Outer . |
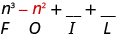 |
| Multiply the Inner . |
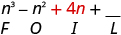 |
| Multiply the Last . |
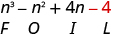 |
| Combine like terms—there are none. |
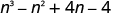 |
Multiply:
 |
||
| Multiply the First . |
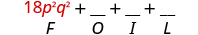 |
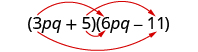 |
| Multiply the Outer . |
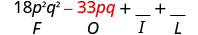 | |
| Multiply the Inner . |
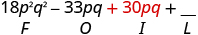 |
|
| Multiply the Last . |
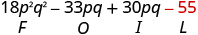 |
|
| Combine like terms—there are none. |
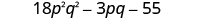 |
The FOIL method is usually the quickest method for multiplying two binomials, but it only works for binomials. You can use the Distributive Property to find the product of any two polynomials. Another method that works for all polynomials is the Vertical Method. It is very much like the method you use to multiply whole numbers. Look carefully at this example of multiplying two-digit numbers.

Now we’ll apply this same method to multiply two binomials.
Multiply using the Vertical Method:
It does not matter which binomial goes on the top.
Notice the partial products are the same as the terms in the FOIL method.
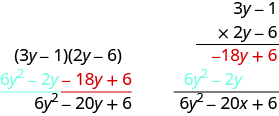
We have now used three methods for multiplying binomials. Be sure to practice each method, and try to decide which one you prefer. The methods are listed here all together, to help you remember them.
To multiply binomials, use the:
Remember, FOIL only works when multiplying two binomials.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?