| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
Let’s use the general strategy for solving linear equations introduced earlier to solve the equation, .
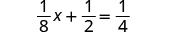 | |
| To isolate the term, subtract from both sides. |
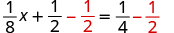 |
| Simplify the left side. |
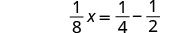 |
| Change the constants to equivalent fractions with the LCD. |
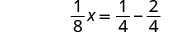 |
| Subtract. |
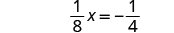 |
| Multiply both sides by the reciprocal of . |
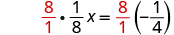 |
| Simplify. |
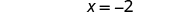 |
This method worked fine, but many students do not feel very confident when they see all those fractions. So, we are going to show an alternate method to solve equations with fractions. This alternate method eliminates the fractions.
We will apply the Multiplication Property of Equality and multiply both sides of an equation by the least common denominator of all the fractions in the equation. The result of this operation will be a new equation, equivalent to the first, but without fractions. This process is called “clearing” the equation of fractions.
Let’s solve a similar equation, but this time use the method that eliminates the fractions.
Notice in [link] , once we cleared the equation of fractions, the equation was like those we solved earlier in this chapter. We changed the problem to one we already knew how to solve! We then used the General Strategy for Solving Linear Equations.
Solve: .
We want to clear the fractions by multiplying both sides of the equation by the LCD of all the fractions in the equation.
| Find the LCD of all fractions in the equation. |
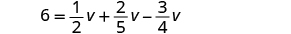 | |
| The LCD is 20. | ||
| Multiply both sides of the equation by 20. |
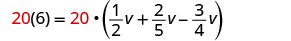 | |
| Distribute. |
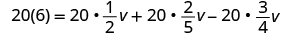 | |
| Simplify—notice, no more fractions! |
 | |
| Combine like terms. |
 | |
| Divide by 3. |
 | |
| Simplify. |
 | |
| Check: |
 |
|
| Let . |
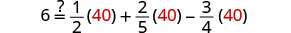 |
|
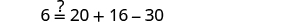 |
||
 |
In the next example, we again have variables on both sides of the equation.
Solve: .
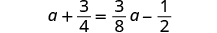 | ||
| Find the LCD of all fractions in the equation.
The LCD is 8. |
||
| Multiply both sides by the LCD. |
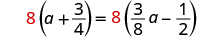 | |
| Distribute. |
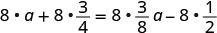 | |
| Simplify—no more fractions. |
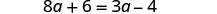 | |
| Subtract from both sides. |
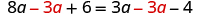 | |
| Simplify. |
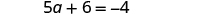 | |
| Subtract 6 from both sides. |
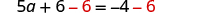 | |
| Simplify. |
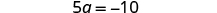 | |
| Divide by 5. |
 | |
| Simplify. |
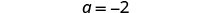 | |
| Check: |
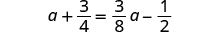 |
|
| Let . |
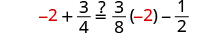 |
|
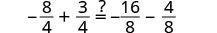 |
||
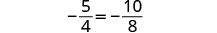 |
||
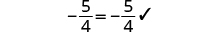 |
In the next example, we start by using the Distributive Property. This step clears the fractions right away.
Solve: .
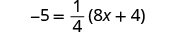 | ||
| Distribute. |
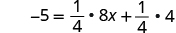 | |
| Simplify.
Now there are no fractions. |
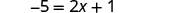 | |
| Subtract 1 from both sides. |
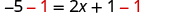 | |
| Simplify. |
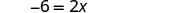 | |
| Divide by 2. |
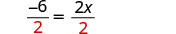 | |
| Simplify. |
 | |
| Check: |
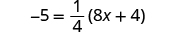 |
|
| Let . |
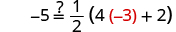 |
|
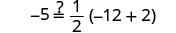 |
||
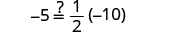 |
||
 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?