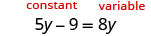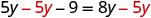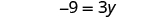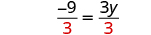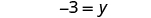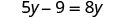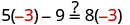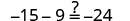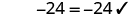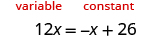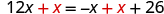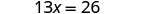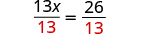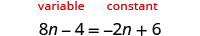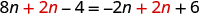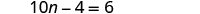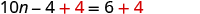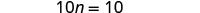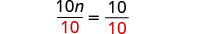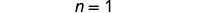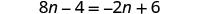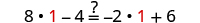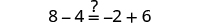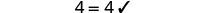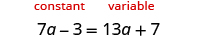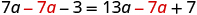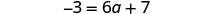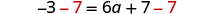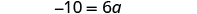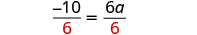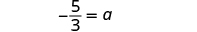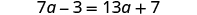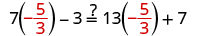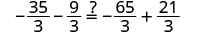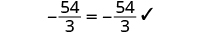-
Home
- Elementary algebra
- Solving linear equations and
- Solve equations with variables
Solve equations with variables and constants on both sides
The next example will be the first to have variables and constants on both sides of the equation. It may take several steps to solve this equation, so we need a clear and organized strategy.
We’ll list the steps below so you can easily refer to them. But we’ll call this the ‘Beginning Strategy’ because we’ll be adding some steps later in this chapter.
Beginning strategy for solving equations with variables and constants on both sides of the equation.
- Choose which side will be the “variable” side—the other side will be the “constant” side.
- Collect the variable terms to the “variable” side of the equation, using the Addition or Subtraction Property of Equality.
- Collect all the constants to the other side of the equation, using the Addition or Subtraction Property of Equality.
- Make the coefficient of the variable equal 1, using the Multiplication or Division Property of Equality.
- Check the solution by substituting it into the original equation.
In Step 1, a helpful approach is to make the “variable” side the side that has the variable with the larger coefficient. This usually makes the arithmetic easier.
Questions & Answers
Three charges q_{1}=+3\mu C, q_{2}=+6\mu C and q_{3}=+8\mu C are located at (2,0)m (0,0)m and (0,3) coordinates respectively. Find the magnitude and direction acted upon q_{2} by the two other charges.Draw the correct graphical illustration of the problem above showing the direction of all forces.
To solve this problem, we need to first find the net force acting on charge q_{2}. The magnitude of the force exerted by q_{1} on q_{2} is given by F=\frac{kq_{1}q_{2}}{r^{2}} where k is the Coulomb constant, q_{1} and q_{2} are the charges of the particles, and r is the distance between them.
Muhammed
What is the direction and net electric force on q_{1}= 5µC located at (0,4)r due to charges q_{2}=7mu located at (0,0)m and q_{3}=3\mu C located at (4,0)m?
what is the change in momentum of a body?
Capacitor is a separation of opposite charges using an insulator of very small dimension between them. Capacitor is used for allowing an AC (alternating current) to pass while a DC (direct current) is blocked.
Gautam
A motor travelling at 72km/m on sighting a stop sign applying the breaks such that under constant deaccelerate in the meters of 50 metres what is the magnitude of the accelerate
What is Thermodynamics
Muordit
velocity can be 72 km/h in question. 72 km/h=20 m/s, v^2=2.a.x , 20^2=2.a.50, a=4 m/s^2.
Mehmet
A boat travels due east at a speed of 40meter per seconds across a river flowing due south at 30meter per seconds. what is the resultant speed of the boat
50 m/s due south east
Someone
which has a higher temperature, 1cup of boiling water or 1teapot of boiling water which can transfer more heat 1cup of boiling water or 1 teapot of boiling water explain your . answer
I believe temperature being an intensive property does not change for any amount of boiling water whereas heat being an extensive property changes with amount/size of the system.
Someone
temperature for any amount of water to boil at ntp is 100⁰C (it is a state function and and intensive property) and it depends both will give same amount of heat because the surface available for heat transfer is greater in case of the kettle as well as the heat stored in it but if you talk.....
Someone
about the amount of heat stored in the system then in that case since the mass of water in the kettle is greater so more energy is required to raise the temperature b/c more molecules of water are present in the kettle
Someone
physics, biology and chemistry
this is my Field
ALIYU
field is a region of space under the influence of some physical properties
Collete
what is ogarnic chemistry
determine the slope giving that 3y+ 2x-14=0
WISDOM
Another formula for Acceleration
pratica A on solution of hydro chloric acid,B is a solution containing 0.5000 mole ofsodium chlorid per dm³,put A in the burret and titrate 20.00 or 25.00cm³ portion of B using melting orange as the indicator. record the deside of your burret tabulate the burret reading and calculate the average volume of acid used?
how do lnternal energy measures
Esrael
Two bodies attract each other electrically. Do they both have to be charged? Answer the same question if the bodies repel one another.
No. According to Isac Newtons law. this two bodies maybe you and the wall beside you.
Attracting depends on the mass och each body and distance between them.
Dlovan
Are you really asking if two bodies have to be charged to be influenced by Coulombs Law?
Robert
like charges repel while unlike charges atttact
Raymond
What is specific heat capacity
Specific heat capacity is a measure of the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin). It is measured in Joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg°C).
AI-Robot
specific heat capacity is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius or kelvin
ROKEEB
Got questions? Join the online conversation and get instant answers!
Source:
OpenStax, Elementary algebra. OpenStax CNX. Jan 18, 2017 Download for free at http://cnx.org/content/col12116/1.2
Google Play and the Google Play logo are trademarks of Google Inc.