| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It should be noted that, if the degree of the numerator is larger than the degree of the denominator by more than one, the end behavior of the graph will mimic the behavior of the reduced end behavior fraction. For instance, if we had the function
with end behavior
the end behavior of the graph would look similar to that of an even polynomial with a positive leading coefficient.
The horizontal asymptote of a rational function can be determined by looking at the degrees of the numerator and denominator.
For the functions listed, identify the horizontal or slant asymptote.
For these solutions, we will use

The quotient is and the remainder is 13. There is a slant asymptote at
In the sugar concentration problem earlier, we created the equation
Find the horizontal asymptote and interpret it in context of the problem.
Both the numerator and denominator are linear (degree 1). Because the degrees are equal, there will be a horizontal asymptote at the ratio of the leading coefficients. In the numerator, the leading term is with coefficient 1. In the denominator, the leading term is with coefficient 10. The horizontal asymptote will be at the ratio of these values:
This function will have a horizontal asymptote at
This tells us that as the values of t increase, the values of will approach In context, this means that, as more time goes by, the concentration of sugar in the tank will approach one-tenth of a pound of sugar per gallon of water or pounds per gallon.
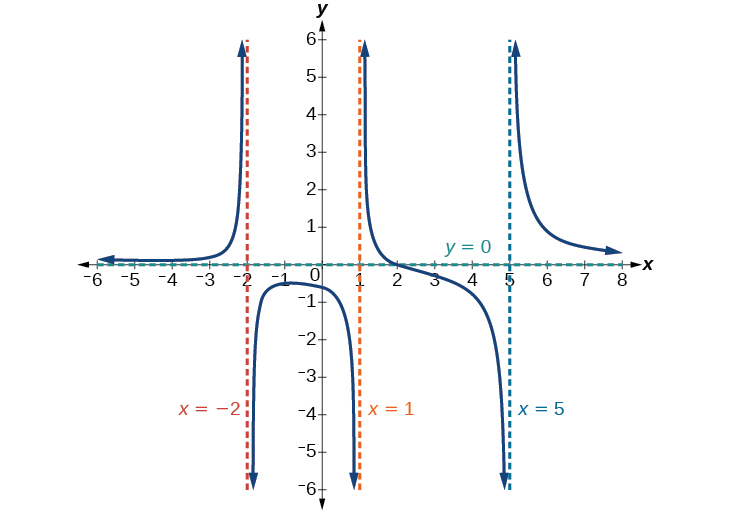
Find the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of the function
First, note that this function has no common factors, so there are no potential removable discontinuities.
The function will have vertical asymptotes when the denominator is zero, causing the function to be undefined. The denominator will be zero at indicating vertical asymptotes at these values.
The numerator has degree 2, while the denominator has degree 3. Since the degree of the denominator is greater than the degree of the numerator, the denominator will grow faster than the numerator, causing the outputs to tend towards zero as the inputs get large, and so as This function will have a horizontal asymptote at See [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?