| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Antimony reacts readily with stoichiometric amounts of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine, yielding trihalides or, with excess fluorine or chlorine, forming the pentahalides SbF 5 and SbCl 5 . Depending on the stoichiometry, it forms antimony(III) sulfide, Sb 2 S 3 , or antimony(V) sulfide when heated with sulfur. As expected, the metallic nature of the element is greater than that of arsenic, which lies immediately above it in group 15.
Boron trihalides—BF 3 , BCl 3 , BBr 3 , and BI 3 —can be prepared by the direct reaction of the elements. These nonpolar molecules contain boron with sp 2 hybridization and a trigonal planar molecular geometry. The fluoride and chloride compounds are colorless gasses, the bromide is a liquid, and the iodide is a white crystalline solid.
Except for boron trifluoride, the boron trihalides readily hydrolyze in water to form boric acid and the corresponding hydrohalic acid. Boron trichloride reacts according to the equation:
Boron trifluoride reacts with hydrofluoric acid, to yield a solution of fluoroboric acid, HBF 4 :
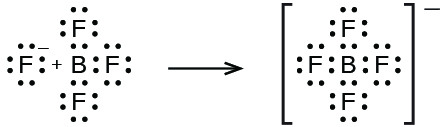
In this reaction, the BF 3 molecule acts as the Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor) and accepts a pair of electrons from a fluoride ion:
All the tetrahalides of silicon, SiX 4 , have been prepared. Silicon tetrachloride can be prepared by direct chlorination at elevated temperatures or by heating silicon dioxide with chlorine and carbon:
Silicon tetrachloride is a covalent tetrahedral molecule, which is a nonpolar, low-boiling (57 °C), colorless liquid.
It is possible to prepare silicon tetrafluoride by the reaction of silicon dioxide with hydrofluoric acid:
Hydrofluoric acid is the only common acid that will react with silicon dioxide or silicates. This reaction occurs because the silicon-fluorine bond is the only bond that silicon forms that is stronger than the silicon-oxygen bond. For this reason, it is possible to store all common acids, other than hydrofluoric acid, in glass containers.
Except for silicon tetrafluoride, silicon halides are extremely sensitive to water. Upon exposure to water, SiCl 4 reacts rapidly with hydroxide groups, replacing all four chlorine atoms to produce unstable orthosilicic acid, Si(OH) 4 or H 4 SiO 4 , which slowly decomposes into SiO 2 .
Boron burns at 700 °C in oxygen, forming boric oxide, B 2 O 3 . Boric oxide is necessary for the production of heat-resistant borosilicate glass, like that shown in [link] and certain optical glasses. Boric oxide dissolves in hot water to form boric acid, B(OH) 3 :


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?