| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Properties of Subatomic Particles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Location | Charge (C) | Unit Charge | Mass (amu) | Mass (g) |
| electron | outside nucleus | −1.602 10 −19 | 1− | 0.00055 | 0.00091 10 −24 |
| proton | nucleus | 1.602 10 −19 | 1+ | 1.00727 | 1.67262 10 −24 |
| neutron | nucleus | 0 | 0 | 1.00866 | 1.67493 10 −24 |
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is its atomic number (Z) . This is the defining trait of an element: Its value determines the identity of the atom. For example, any atom that contains six protons is the element carbon and has the atomic number 6, regardless of how many neutrons or electrons it may have. A neutral atom must contain the same number of positive and negative charges, so the number of protons equals the number of electrons. Therefore, the atomic number also indicates the number of electrons in an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is called its mass number (A) . The number of neutrons is therefore the difference between the mass number and the atomic number: A – Z = number of neutrons.
Atoms are electrically neutral if they contain the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons. When the numbers of these subatomic particles are not equal, the atom is electrically charged and is called an ion . The charge of an atom is defined as follows:
Atomic charge = number of protons − number of electrons
As will be discussed in more detail later in this chapter, atoms (and molecules) typically acquire charge by gaining or losing electrons. An atom that gains one or more electrons will exhibit a negative charge and is called an anion . Positively charged atoms called cations are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. For example, a neutral sodium atom (Z = 11) has 11 electrons. If this atom loses one electron, it will become a cation with a 1+ charge (11 − 10 = 1+). A neutral oxygen atom (Z = 8) has eight electrons, and if it gains two electrons it will become an anion with a 2− charge (8 − 10 = 2−).
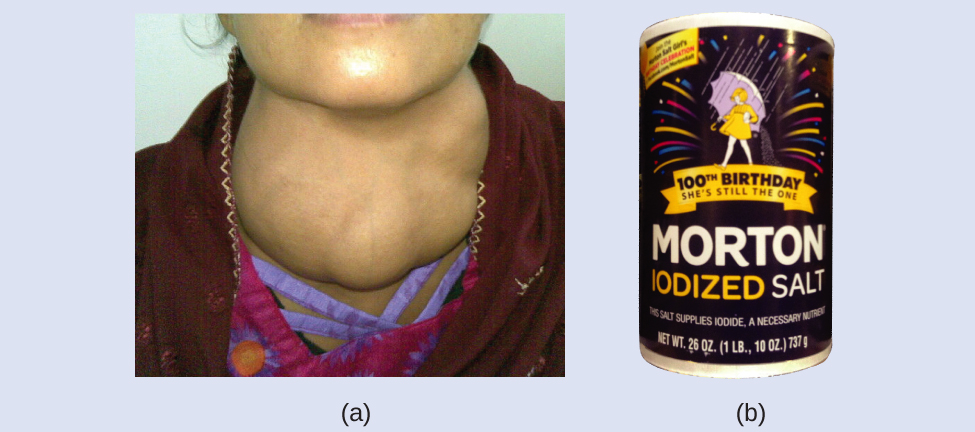
The addition of small amounts of iodine to table salt (iodized salt) has essentially eliminated this health concern in the United States, but as much as 40% of the world’s population is still at risk of iodine deficiency. The iodine atoms are added as anions, and each has a 1− charge and a mass number of 127. Determine the numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons in one of these iodine anions.
78 protons; 117 neutrons; charge is 4+

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?