| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The thalamus (Greek for “inner chamber”), illustrated in [link] , acts as a gateway to and from the cortex. It receives sensory and motor inputs from the body and also receives feedback from the cortex. This feedback mechanism can modulate conscious awareness of sensory and motor inputs depending on the attention and arousal state of the animal. The thalamus helps regulate consciousness, arousal, and sleep states. A rare genetic disorder called fatal familial insomnia causes the degeneration of thalamic neurons and glia. This disorder prevents affected patients from being able to sleep, among other symptoms, and is eventually fatal.
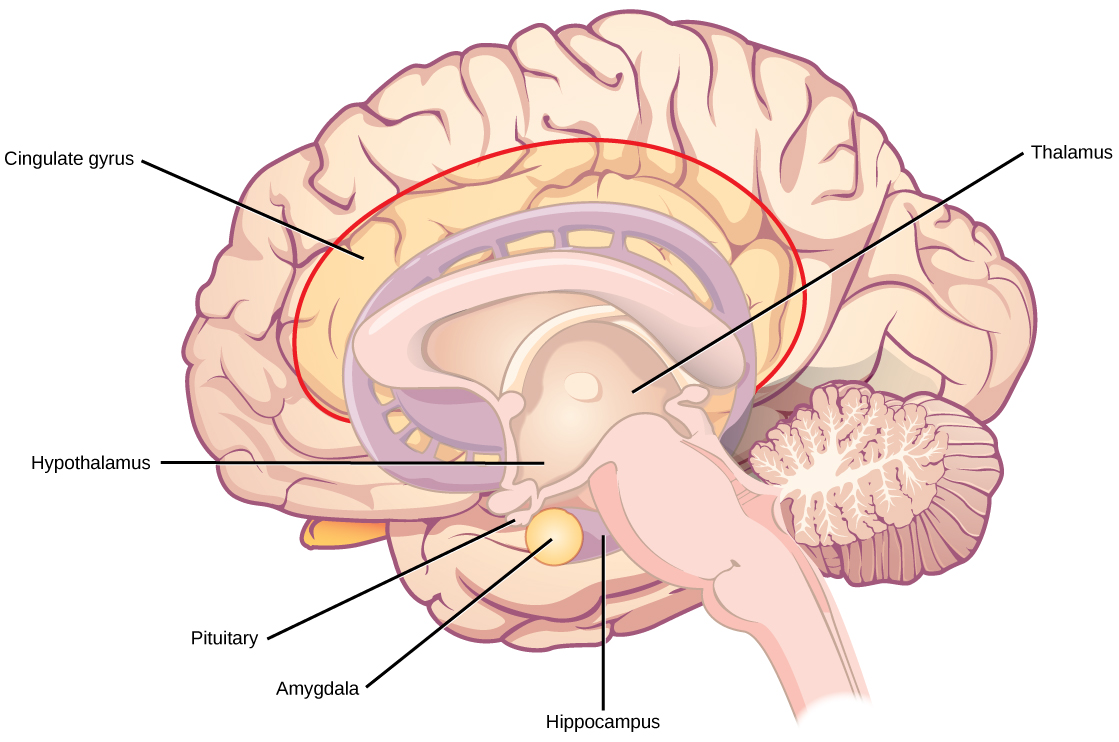
Below the thalamus is the hypothalamus , shown in [link] . The hypothalamus controls the endocrine system by sending signals to the pituitary gland, a pea-sized endocrine gland that releases several different hormones that affect other glands as well as other cells. This relationship means that the hypothalamus regulates important behaviors that are controlled by these hormones. The hypothalamus is the body’s thermostat—it makes sure key functions like food and water intake, energy expenditure, and body temperature are kept at appropriate levels. Neurons within the hypothalamus also regulate circadian rhythms, sometimes called sleep cycles.
The limbic system is a connected set of structures that regulates emotion, as well as behaviors related to fear and motivation. It plays a role in memory formation and includes parts of the thalamus and hypothalamus as well as the hippocampus. One important structure within the limbic system is a temporal lobe structure called the amygdala (Greek for “almond”), illustrated in [link] . The two amygdala are important both for the sensation of fear and for recognizing fearful faces. The cingulate gyrus helps regulate emotions and pain.
The cerebellum (Latin for “little brain”), shown in [link] , sits at the base of the brain on top of the brainstem. The cerebellum controls balance and aids in coordinating movement and learning new motor tasks.
The brainstem , illustrated in [link] , connects the rest of the brain with the spinal cord. It consists of the midbrain, medulla oblongata, and the pons. Motor and sensory neurons extend through the brainstem allowing for the relay of signals between the brain and spinal cord. Ascending neural pathways cross in this section of the brain allowing the left hemisphere of the cerebrum to control the right side of the body and vice versa. The brainstem coordinates motor control signals sent from the brain to the body. The brainstem controls several important functions of the body including alertness, arousal, breathing, blood pressure, digestion, heart rate, swallowing, walking, and sensory and motor information integration.
Connecting to the brainstem and extending down the body through the spinal column is the spinal cord , shown in [link] . The spinal cord is a thick bundle of nerve tissue that carries information about the body to the brain and from the brain to the body. The spinal cord is contained within the bones of the vertebrate column but is able to communicate signals to and from the body through its connections with spinal nerves (part of the peripheral nervous system). A cross-section of the spinal cord looks like a white oval containing a gray butterfly-shape, as illustrated in [link] . Myelinated axons make up the “white matter” and neuron and glial cell bodies make up the “gray matter.” Gray matter is also composed of interneurons, which connect two neurons each located in different parts of the body. Axons and cell bodies in the dorsal (facing the back of the animal) spinal cord convey mostly sensory information from the body to the brain. Axons and cell bodies in the ventral (facing the front of the animal) spinal cord primarily transmit signals controlling movement from the brain to the body.
The spinal cord also controls motor reflexes. These reflexes are quick, unconscious movements—like automatically removing a hand from a hot object. Reflexes are so fast because they involve local synaptic connections. For example, the knee reflex that a doctor tests during a routine physical is controlled by a single synapse between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron. While a reflex may only require the involvement of one or two synapses, synapses with interneurons in the spinal column transmit information to the brain to convey what happened (the knee jerked, or the hand was hot).
In the United States, there around 10,000 spinal cord injuries each year. Because the spinal cord is the information superhighway connecting the brain with the body, damage to the spinal cord can lead to paralysis. The extent of the paralysis depends on the location of the injury along the spinal cord and whether the spinal cord was completely severed. For example, if the spinal cord is damaged at the level of the neck, it can cause paralysis from the neck down, whereas damage to the spinal column further down may limit paralysis to the legs. Spinal cord injuries are notoriously difficult to treat because spinal nerves do not regenerate, although ongoing research suggests that stem cell transplants may be able to act as a bridge to reconnect severed nerves. Researchers are also looking at ways to prevent the inflammation that worsens nerve damage after injury. One such treatment is to pump the body with cold saline to induce hypothermia. This cooling can prevent swelling and other processes that are thought to worsen spinal cord injuries.

The vertebrate central nervous system contains the brain and the spinal cord, which are covered and protected by three meninges. The brain contains structurally and functionally defined regions. In mammals, these include the cortex (which can be broken down into four primary functional lobes: frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal), basal ganglia, thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, cerebellum, and brainstem—although structures in some of these designations overlap. While functions may be primarily localized to one structure in the brain, most complex functions, like language and sleep, involve neurons in multiple brain regions. The spinal cord is the information superhighway that connects the brain with the rest of the body through its connections with peripheral nerves. It transmits sensory and motor input and also controls motor reflexes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?